Current Affairs Of Today
1) BRO Road to the Nation in East Sikkim – A Fillip to Defence Preparedness and Socio-Economic Development
- Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh was in Sikkim to dedicate the 19.85 Km Alternate Alignment of the National Highway 310 from km 0.00 to km 19.350 to the Nation. Necessitated due to the previous alignment having seen extensive damages due to sinking and other natural hazards, the road serves as an important link to bolster defense preparedness in the Nathula Sector in particular and in the whole of East Sikkim in general. The Raksha Mantri while addressing the gathering on the occasion complimented the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) for its unwavering commitment towards delivering outstanding quality infrastructure in record time and optimal costs.
- Raksha Mantri enumerated the Government’s drive towards progressing infrastructure development in far-flung areas not only enhance defense preparedness but also fostering socio-economic development of the region. Reiterating the Centre’s resolve to speed up infrastructure development in alignment with Prime Minister’s Act North-East policy, the Minister highlighted the pace at which construction of the alternate alignment, which had been held up since commencement in 2009, was facilitated over the last two years. The Chief Minister of Sikkim Shri Prem Singh Tamang brought out the positive impact of the new alignment that will be boosting tourism as well as the socio-economic development of the state. Emphasizing that tourism is the main bulwark of the state’s economy, the Chief Minister was highly appreciative of the BRO and the Central Government for completing the road expeditiously.
- The BRO over the last some years has undertaken an unprecedented expansion of its capabilities through technology infusion in material, equipment, and construction techniques. The Atal Tunnel, DS-DBO Road, the new alignment of the National Highway 310 are examples of high quality, fast-paced results delivered by the BRO towards strategic and operational preparedness. The Raksha Mantri also highlighted the future works that the BRO is to undertake and expressed confidence that the mission of Aatmanirbhar Bharat will progress by leaps and bounds in the years ahead.
Source:
PIB
2) New age sustainable disinfectants and sanitizers may bring relief from chemical ones with side effects
- The days of suffering from dry, itching hands due to rinsing them multiple times with chemical disinfectants and soap as protection against contact infection of COVID 19 may soon be over. Several start-ups based in different parts of India are now armed with a range of sustainable alternatives to conventional chemical-based decontaminants that can disinfect surfaces and even microcavities.
- They also include technologies for disinfection of the biomedical waste generated at hospitals and the use of novel nanomaterials and chemical process innovations for long-lasting & safe sterilization of the recurrent use surfaces.
- Safe disinfection and sanitization technologies have come from a total of 10 companies supported for disinfectants and sanitizers under Centre for Augmenting WAR with COVID-19 Health Crisis (CAWACH), an initiative by the National Science & Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board (NSTEDB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), implemented by Society for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (SINE), IIT Bombay.
- Mumbai based start-up Inphlox Water Systems, with expertise in treating complex polluted water and wastewater, modified their technology to design and develop a system for space and equipment disinfection to fight COVID 19 contamination titled VAJRA. The VAJRA KE Series uses a disinfection system consisting of a multistage disinfection process by incorporating electrostatic discharge that generates ozone, and the powerful sterilizing effects of the UVC light spectrum. VAJRA Kavach-E (KE) uses advanced oxidation, electrostatic discharge, and UVC light spectrum to inactivate the viruses, bacteria, and other microbial strains present on the PPE. This saves costs by making the PPE, medical, and nonmedical gear reusable.
- Inphlox Water Systems, which started with the Nidhi Prayas grant from DST (through IIT Bombay) for innovations in the water sector, used the CAWACH grant from DST to modify their technology to make it suitable for combating the COVID 19 infection. They prepared themselves for manufacturing 25 space disinfection systems per month, streamlined the production, supply chain, and logistics to scaling up the manufacturing capacity by 25% with each passing month thereon.
- At present, they are coordinating with IIT Bombay’s and CCMB’s (Hyderabad) virology labs for further testing of these systems. The startup is ready with commercial product versions and is working on improving product certifications so that specialized labs can also use their solutions.
- Coimbatore based Eta Purification offers advanced sterilization solutions. It is using environmentally-sound micro-cavity plasma technology. This novel technology, where the disinfectant is produced directly from air or oxygen offers a sustainable alternative to conventional chemical-based decontamination.
- The COSMO (Complete Sterilization by Microplasma Oxidation) system can rapidly disinfect Covid-19 infected areas, including quarantine facilities, ambulatory care, and equipment surfaces. This innovative micro-plasma sterilization system offers compact and scalable modular units that are robust, flexible, and energy-efficient.
- The disinfectant is produced on-site, thereby eliminating the transport, storage, and handling of hazardous chemicals. These decontamination systems are 10 times less than the conventional system of equivalent capacity, making it suitable for resource constraint environments. Their advanced sterilization systems surpass hypochlorite and other traditional disinfectants in its ability to neutralize multi-drug resistant pathogens. The company has already provided customized solutions to hospitals and healthcare settings to sterilize selective critical care areas.
- They have also taken this innovation to vulnerable communities. Presently their advanced integrated micro-plasma oxidation system for rapid sterilization has been fully developed and tested rigorously for commercial use.
- A mechanical hand sanitizing dispenser machine which quantifies the steps of hand sanitization through touchless, real-time monitoring via dashboard is offered by Chennai based startup MicroGO.
- We innovate Biosolutions from Pune has developed silver nanoparticles based on non-alcoholic liquid sanitizer. Their technology pending for patent also inhibits the RNA replication activity – preventing the spread of the virus and blocks surface glycoproteins – making the virus ineffective.
- An instant microwave-based handheld sterilizer ATULYA and a microwave-assisted cold sterilization device OPTIMASER for hazardous biomedical waste disinfection and making linen and PPE reusable is the offering from Lucknow based Maser Technology.
- OPTIMIZER is microwave-assisted cold sterilization superior technological advancement over the conventional Autoclave. It allows for disinfection and sterilization of the PPE Kits and the masks to ensure the 100 reusabilities, also ensuring the cost-effectiveness of the same. ANTALYA is an Instant Microwave based handheld sterilizer which offers the cutting edge over the UV tube-based sterilizer, sanitizing sprays & all the possible methods of sterilization & protection.
- Incubators like SINE IIT Bombay FIIT, IIT Delhi, SIIC, IIT Kanpur, HTIC, IIT Madras, Venture Centre, Pune, IKP Knowledge Park, Hyderabad, KIIT-TBI, Bhubaneswar provided timely advice on technical progress, guided the startups to follow all necessary guidelines, signing of MoUs and so on.
Source:
PIB
3) Newly identified tectonically active zone in the Himalayas could alter earthquake study & predictions
- The suture zone of the Himalayas or the Indus Suture Zone (ISZ) in the Ladakh region where Indian and Asian Plates are joined is tectonically active, as against current understanding that it is a locked zone.
- This could have major implications in terms of earthquake study, prediction, understanding the seismic structure of the mountain chains well as its evolution.
- A group of Scientists from Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology (WIHG), Dehradun, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, have found through observations and detailed mapping of geological features that the suture zone of Himalaya that was conventionally thought to be locked is tectonically active. They carried out the mapping of the remote regions of Ladakh that forms the most hinterland part of the Himalayas. The study was published recently in the journal ‘Technophysics’.
- The geologists observed that sedimentary beds are tilted and thrust broken, the rivers are associated with uplifted terraces, and the bedrock shows brittle deformation that occurred at much shallower depths. These deformed geological features were then dated in the laboratory at Dehradun using a technique called Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) (method for carrying Luminescence dating of geological sediments) and data of seismicity and denudation rate reviewed. The combination of field and lab data suggested the region of the Indus Suture Zone (ISZ) has been neo-tectonically active since the last 78000 -- 58000 years and a recent earthquake in 2010 of low magnitude 4.0 near the village of Upshi that occurred due to a thrust rupture.
- Himalaya was known to be made up of north dipping thrusts like the Main Central Thrust (MCT), the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), and the Main Frontal Thrust (MFT). As per the established models, all of these thrusts except MFT are locked, and the overall deformation in Himalaya is being accommodated only along with the MFT. The new findings, which suggest a more remote fault at the suture zone being neo-tectonically active, could call for a serious relook into the existing evolutionary models using new techniques and a larger geological database.
Source:
PIB
4) Australia Circular Economy Hackathon(I-ACE)
- AIM (Atal Innovation Mission), in association with CSIRO, is organizing a two-day hackathon on the circular economy, ‘India–Australia Circular Economy Hackathon (I-ACE)’, on 7 and 8 December.
- The idea of I-ACE was conceived during a virtual summit on 4 June, between the Indian and Australian prime ministers, exploring innovative ways to boost the circular economy in India and Australia.
- I-ACE will focus on the identification and development of innovative technology solutions by bright-minded students, startups, and MSMEs of both nations.
- The four key themes for the hackathon are as follows:
- Innovation in packaging reducing packaging waste
- Innovation in food supply chains avoiding waste
- Creating opportunities for plastic waste reduction
- Recycling critical energy metals and e-waste
-
Shortlisted students and startups/MSMEs will be called for the hackathon,
where two winners (one student and one startup/MSME) per theme from each
country will be announced at an award ceremony on 11 December.
- The winning Indian student and startup/MSME teams will be awarded a prize of Rs 2 lakh and Rs 5 lakh, respectively, coupled with post-hackathon product development opportunities. The winning Australian student will be awarded a prize of AUD$3500 and the winning Australian SMEs/startup team a prize of AUD$9500.
Source:
PIB
5) India against tsunami threat
- India is much safer against the threat of tsunamis than it was in 2004, thanks to the stateoftheart tsunami early warning system established in the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS). However, the best of warning systems could fail, if communities are not prepared, if they do not understand the official and natural warning signs of a tsunami, and if they do not take appropriate and timely response
- We have made impressive progress in building tsunami early warning capability. From absolutely no warning capability or for that matter any public knowledge of tsunamis in the Indian Ocean, we have reached a stage where we can detect large undersea earthquakes in realtime and provide a tsunami warning in 10-20 minutes after the earthquake occurrence. In fact, for Indian Ocean earthquakes where the network of seismometers is reasonably good, quakes can now be detected in less than five minutes and a tsunami warning issued within 10 minutes if the quake occurs elsewhere in the globe
- The focus in recent times has been on enhancing community awareness and response through several capacity-building activities, biennial Indian Oceanwide tsunami drills, and piloting of the UNESCO-IOC Tsunami Ready initiative to provide a structured framework to build and measure capacities of coastal communities to respond effectively to tsunamis, through 11 important indicators.
- Two villages — Venkatraipur in Ganjam district and Noliasahi in Jagatsingpur district in Odisha — are now ‘TsunamiReady’. “This has to be replicated in other vulnerable coastal communities as it also enhances the ability to respond to cyclones and storm surges too
Source:
The Hindu
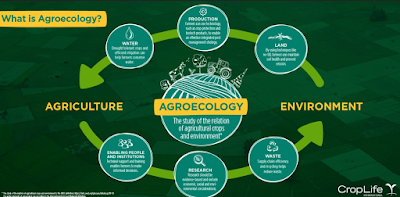
6) What is Agroecology?
- Agroecology is farming that centers on food production that makes the best use of nature’s goods and services while not damaging these resources. Farming thrives when it works with local ecosystems, for example, improving soil and plant quality through available biomass and biodiversity, rather than battling nature with chemical inputs.
7) Compound Interest Waiver on Moratorium Loans
- Recently, the Government of India has announced the scheme for the waiver of compound interest that was payable by the borrower who had opted for loan moratorium between 1st March 2020, and 31st August 2020.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had in March 2020 offered a three-month moratorium on loans, enabling borrowers to defer repayments on EMIs and other loans. This was later extended by another three months, till 31st August 2020.
- The loan moratorium, and waiver of compound interest, was aimed at providing borrowers relief amid the economic impact of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Compound Interest Waiver Scheme:
- Under this, the government will grant eligible borrowers ex-gratia payment of the difference between the compound interest and simple interest for the six-month moratorium period.
- Ex-gratia payment is the money that is paid due to moral obligation and not due to legal obligation.
- Simple interest is levied only on the principal amount of a loan or deposit. In contrast, compound interest is levied on the principal amount and the interest that accumulates on it in every period.
Eligibility:
- The scheme shall be applicable for loans availed by Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) as well as loans to retail customers for education, housing, consumer durables, automobiles, provided a borrower has an aggregate outstanding loan of Rs. 2 crores or less, from all such loans.
- Credit card dues have also been included in the scheme’s ambit.
- The loan interest waiver payment shall be admissible, irrespective of whether the borrower had availed the moratorium partly, fully, or not at all.
- However, this would only be permitted for loan accounts that had not been reported as Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) as of 29th February 2020.
- A loan is recorded as a non-performing asset or NPA, 90 days after repayments become overdue.
Effect:
- The amount saved through the loan interest waiver will be very small. This is because only the interest that would have been charged on the interest of the original loan during the six months moratorium period is waived off.
- In other words, the loan repayment will continue and one will still need to pay the simple interest that would have paid if not opted for the loan moratorium.
- It is only the compounding interest that goes off.
Implementation:
- Lenders have been asked to set up a grievance redressal mechanism for eligible borrowers under the scheme by 30th October 2020.
- A mechanism has also been put in place for lenders to claim the amount back from the government. Lenders have to submit claims for reimbursement by 15th December 2020 through a special cell set up in the State Bank of India (SBI).
Source:
The Hindu
8) Indira Rasoi Yojana: Rajasthan
- Recently, over 50 lakh people have benefited from Indira Rasoi Yojana (a kitchen scheme), in Rajasthan. The scheme was launched in August 2020.
- Aim: To provide nutritious food to the poor and needy twice a day at concessional rates.
- Under the scheme, each plate serves 100 grams of pulses and vegetables each, 250 grams of chapati and pickles.
- It aligns with the World Food Day’s 2020 theme to grow, nourish and sustain together.
- Implementation: The local voluntary organizations have been roped in for establishing the centres near the places such as bus stands, railway stations and hospitals and for successful implementation of the scheme.
- Background: The current Rajasthan government scrapped the previous Annapurna Rasoi Yojana which was offering breakfast and lunch on the lines of Tamil Nadu’s Amma Unavagam (mother’s canteen).
- Monitoring: A committee headed by the District Collector will be monitoring the implementation of the scheme. A special app has also been created for monitoring the food quality.
- Target: The scheme targets to serve 1.34 lakh people per day in the state. Till now the scheme has benefitted 50.30 lakh, persons, across the State.
Source:
The Hindu
9) India’s First Seaplane Project
- India's first seaplane service in Gujarat is set to start from 31st October 2020, the birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, with the aim of providing air connectivity between the Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad and the Statue of Unity in Kevadia.
- The seaplane will be operated by SpiceJet. It is a 19-seater seaplane, which will be able to accommodate 14 passengers.
- In the next phase, the Dharoi dam (Mehsana district) will connect Ambaji and Shatrunjay dam (Bhavnagar district) and Tapi district.
Seaplane:
- A seaplane is a fixed-wing airplane designed for taking off and landing on water.
- There are two main types of seaplanes: flying boats (often called hull seaplanes) and floatplanes.
- A flying boat is a fixed-winged seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water, that usually has no type of landing gear to allow operation on land. It differs from a floatplane as it uses a purpose-designed fuselage which can float, granting the aircraft buoyancy
- The bottom of a flying boat’s fuselage is its main landing gear. This is usually supplemented with smaller floats near the wingtips, called wing or tip floats.
- The hull of a flying boat holds the crew, passengers, and cargo; it has many features in common with the hull of a ship or a boat.
- A floatplane is supported on the water by pontoons, called floats.
Countries that Operate Seaplanes:
- Seaplanes are operational in countries like the Philippines, Canada, Australia, the United States, Finland, the United Kingdom, Sri Lanka, Fiji, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, United Arab Emirates, Italy, Maldives, and Hongkong.
- In India, Jal Hans, a commercial seaplane service based in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands was launched as a pilot project in December 2010 with a capacity of 10 passengers.
India's Seaplane Project:
- As per the direction of the Centre, the Airports Authority of India (AAI) requested state governments of Gujarat, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana and the administration of Andaman & Nicobar to propose potential locations for setting up water airports to boost the tourism sector.
- In 2019, the Centre approved flights from six water airports that include Shatrunjay Dam (Gujarat), Guwahati riverfront and Umrangso reservoir (Assam) and Nagarjuna Sagar (Andhra Pradesh), under the third round of Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN) scheme.
- The routes awarded for seaplane operations include Sabarmati riverfront to Statue of Unity and Shatrunjay Dam; Guwahati riverfront to Umrango reservoir, Jorhat and Shillong (Meghalaya) and Nagarjuna Sagar to Vijayawada and Hyderabad (Telangana).
- Agatti, Kavaratti and Minicoy islands of Lakshadweep have also been proposed to be connected through the seaplane project under the fourth round of UDAN scheme.
Benefit:
- The project will lead to an increase in tourism and hotel business at the local level. It will also serve employment to local people.
- The establishment of water airports will contribute to an increase in the level of current social infrastructural facilities at the proposed sites.
Impact on Environment:
- Negative: Experts think that the activities proposed under the water airport project may have a similar type of impact as that of an airport.
- However, the water airport is not a listed project/activity in the Schedule to the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, 2006 nor in EIA draft 2020.
- Positive: During seaplane operations, there will be turbulence created in the water while takeoff and landing of seaplanes.
- This will lead to mixing of oxygen in the water, which will have a positive impact on the aquatic ecosystem near seaplane operations increasing oxygen content and decreasing carbon content in this system.
UDAN Scheme
- Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN) was launched as a regional connectivity scheme under the Ministry of Civil Aviation in 2016.
- The objective of the scheme is to create affordable yet economically viable and profitable flights on regional routes so that flying becomes affordable to the common man even in small towns.
- The scheme envisages providing connectivity to un-served and underserved airports of the country through the revival of existing airstrips and airports. The scheme is operational for a period of 10 years.
- Under-served airports are those which do not have more than one flight a day, while un-served airports are those where there are no operations.
- UDAN 3.0 and UDAN 4.0 aim to include Seaplanes for connecting water airports.
Source:
Indian Express
10) Two New Ramsar Sites
- Recently, Kabartal Wetland (Bihar) and Asan Conservation Reserve (Uttrakhand) have been designated as Ramsar sites, making them ‘Wetlands of International Importance’.
- Earlier in 2020, India designated 10 more wetlands as a Ramsar site, taking the total number from 27 to 37.
- With 2 more inclusions, the total number of Ramsar sites in India is 39, the highest in South Asia.
Kabartal Wetland:
- Also known as Kanwar Jheel, it covers 2,620 hectares of the Indo-Gangetic plains in the Begusarai district of Bihar.
- It acts as a vital flood buffer for the region besides providing livelihood opportunities to local communities.
- Significant biodiversity is present, with 165 plant species and 394 animal species recorded, including 221 bird species. It is also a valuable site for fish biodiversity with over 50 species documented.
- It is an important stopover along the Central Asian Flyway, with 58 migratory waterbirds using it to rest and refuel.
- Five critically endangered species inhabit the site, including three vultures – the red-headed vulture (Sarcogyps calvus), white-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis) and Indian vulture (Gyps indicus) – and two waterbirds, the sociable lapwing (Vanellus gregarious) and Baer’s pochard (Aythya baeri).
- Major threats to the Site include water management activities such as drainage, water abstraction, damming and canalization.
Asan Conservation Reserve:
- ACR is a 444-hectare stretch of the Asan River running down to its confluence with the Yamuna River in the Dehradun district of Uttarakhand. It is Uttarakhand's first Ramsar Site.
- The damming of the River by the Asan Barrage in 1967 resulted in siltation above the dam wall, which helped to create some of the Site’s bird-friendly habitats.
- These habitats support 330 species of birds including the critically endangered red-headed vulture (Sarcogyps calvus), white-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis) and Baer’s pochard (Aythya baeri).
- Other non-avian species present include 49 fish species, one of these being the endangered Putitora mahseer (Tor putitora). Fish use the site for feeding, migration, and spawning.
Ramsar Site
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands is an intergovernmental treaty adopted in 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar, on the southern shore of the Caspian Sea.
- It came into force for India on 1st February 1982. Those wetlands which are of international importance are declared as Ramsar sites.
- The Convention’s mission is “the conservation and wise use of all wetlands through local and national actions and international cooperation, as a contribution towards achieving sustainable development throughout the world”.
- The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution or other human interference. It is maintained as part of the Ramsar List.
- At present, two wetlands of India are in Montreux Record: Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) and Loktak Lake (Manipur).
- Chilika Lake (Odisha) was placed in the record but later removed from it.
Source:
Hindustan Times




Comments
Post a Comment