Current Affairs Of Today Are
1) Harit Path
- The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), a public sector undertaking under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, has developed a mobile App called ‘Harit Path' to monitor location, growth, species details, maintenance activities, targets and achievements of each of its field units for each and every plant under all plantation projects. The app was inaugurated by the Union Minister for RTH Shri Nitin Gadkari
- According to an NHAI release, to commemorate 25 years of its service to the nation, it has also recently undertaken ‘Harit Bharat Sankalp’, a nation-wide plantation drive which is in line with its commitment to promote environmental protection and sustainability. Under this initiative, NHAI planted over 25 lakh plants in 25 days along the stretches of the National Highways between 21st July to 15th August 2020. The drive takes the total cumulative number of plantations done during the current year to 35.22 lakh.
- The nation-wide plantation drive has been actively taken up by NHAI’s regional offices to achieve the collective target of making greener national highways. A maximum number of over 5.0 lakh plants have been planted in Uttar Pradesh, followed by over 3.0 lakh in Rajasthan and 2.67 Lakh in Madhya Pradesh along the national highways. To ensure 100% survival of the plants, avenue plantation of a minimum height of 1.5-meter has been emphasized along the national highway am
- The Release says that to track the growth and health of the plants, photographs along with data of the plants captured using Harit Path shall be uploaded every 3 months on NHAI’s AI-powered Big Data Analytics platform – Data Lake. Highway contractors shall be accountable for the proper upkeep and maintenance of the plantation and liable to replace the missing/dead plants. The performance and growth of the plants shall be linked to the payment to the contractors for this work.
- After the launch of the app, NHAI has immediately started work to create user ids of over 150 ROs/ PDs/ Horticulture experts. Apart from this, around 7800 plants have also been geotagged using the toda
- NHAI has been undertaking plantation drives from time to time to develop eco-friendly National Highways and has constantly addressed ecological concerns by adopting environment-friendly methods. In the year 2020, NHAI plans to undertake a sustained plantation drive. The vision is to plant 72 Lakh plants along NH stretches collectively with the concessionaire, State Government agencies, and private plantation agencies. Also, NHAI is engaging experts from the plantation, forestry, agriculture, horticulture with vast field experience. Two professionals with suitable background and experience are being engaged for each of its regional offices. For proper supervision of plantation in each project, horticulture experts are also being engaged. Apart from the plantation, NHAI is also emphasizing on transplantation of trees that are required to be axed for the development of highway projects.
- NHAI has identified the NH stretches and is creating a database of all the plantations already done and to be done on these stretches. The launch of ‘Harit Path’, a mobile app will further facilitate the creation of Green Highways across the country.
Source:
PIB
2) ARCI scientists convert tamarind waste & cotton waste to supercapacitor electrodes
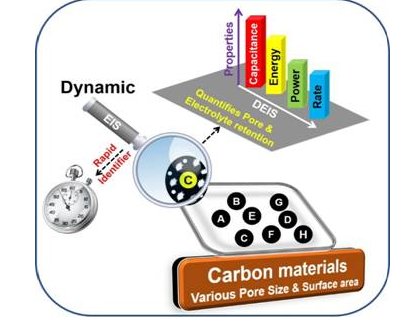
- Tamarind seeds and cotton waste may soon be used to make low-cost supercapacitors for energy storage – thanks to the efforts of a group of Indian scientists who have used such waste biomass to develop materials for making cost-effective supercapacitor devices. This can pave the way towards affordable electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles which bank on supercapacitors significantly for their application in braking systems and start-stop cycles.
- Responding to the intense hunt for supercapacitor materials to meet the widespread demand for supercapacitors, Scientists at the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy & New Materials (ARCI), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India, have developed a couple of cost-effective electrode material for making affordable supercapacitor devices, from waste biomass like tamarind seeds and industrial cotton waste. They have converted the waste materials into highly porous carbon fibers by the activation process and then utilized the porous carbon fibers to make high-performance supercapacitor electrodes.
- The electrode materials made from the biomass waste have been tested with the help of a rapid testing protocol developed by Scientists at Centre for Fuel Cell Technology, ARCI-Chennai to evaluate different porous electrode materials for their suitability in supercapacitors. The protocol involves Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) and records the impedance ( a parameter used to measure the opposition that a circuit presents to a current when a voltage is applied) offered by a material under a small perturbation and the capacitance (ratio of the change in the electric charge of a system to the corresponding change in its electric potential) formed by the arrangement of electrolyte ions over the electrode surface, which is called as double-layer capacitance.
- The ARCI scientists used it to test the pore characteristics and stability of the activated carbon material prepared from tamarind seed and its suitability for supercapacitor applications.
- The Dynamic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (DEIS) results observed by the ARCI team exhibited a superior double layer capacitance value at all the applied potentials for the optimized sample with high surface area (2645 m2 g-1) within 1 hour of the experiment, validating that the material could be used for supercapacitor electrode.
|
| Dynamic Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a rapid screening procedure to identify supercapacitor electrode material |
Source:
PIB
3) Oral nanomedicine may bring relief for Kala-Azar & other neglected diseases
- Patients affected by Kala- Azar, scientifically called Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), one of the most neglected tropical diseases may soon find relief in an oral nanomedicine from India. The oral therapeutics could help in the control and elimination of VL, around 95 % of which is reported from Bangladesh, Brazil, China, Ethiopia, India, Kenya, Nepal, Somalia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
- Scientists from the Institute of Nano Science & Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India, have developed an oral nanomedicine with the help of surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticles based combinational cargo system for combating visceral leishmaniasis. The findings of their study supported by the DST-SERB Early Career Research Award have been recently published in the journals ‘Scientific Reports’ and ‘Materials Science & Engineering C’.
- According to the INST team, till-date there is no study reported where a combination of two anti-leishmanial drugs has been delivered through nanomodification as a potential therapeutic strategy against visceral leishmaniasis. This work suggests the superiority of as-prepared modified formulation (m-DDSLNs) surface modified with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPCD) is a promising approach towards the oral delivery of anti-leishmanial drugs.
- In this study by the INST team led by Dr. Shyam Lal M anti-leishmanial drugs Amphotericin B (AmB) & Paromomycin (PM) were encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles and further modified with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPCD). The scientists explored the oral therapeutic potential of the formulation in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. They employed an emulsion solvent evaporation method to prepare HPCD modified dual drug-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (m-DDSLNs). The nanoparticle-based combinatorial drug delivery system developed by them enhanced the efficacy of the formulation in both in vitro and in vivo models by reducing intracellular amastigote growth in L. donovani-infected macrophages and hepatic parasite burden in L. donovani-infected BALB/c mice model, respectively without causing any significant toxic side effects.
- According to the INST team, the solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) can help enhance the oral uptake of the therapeutic agent by retaining a solubilized state of the drug in the Gastrointestinal Tract and favors the formation of mixed micelles (a special case of solubilization) by inducing the secretion of bile salts and phospholipids. Further, 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPCD) are cyclic oligosaccharides that are known to be molecular hosts which can selectively include water-insoluble guest molecules within their hydrophobic cavity through non-covalent interactions.
- This study by the INST team may lead to product and process patent enhancing the role of our country for developing innovative therapy against neglected diseases. The usage of a lower therapeutic dose of the purified drugs through nanomodifications will be a boon in reducing toxicity, which has been a major hindrance in the existing conventional treatment when administered orally.
Source:
PIB
4) Aarogya Setu introduces ‘Open API Service’
- As we move on to the new normal of learning to live with COVID19, Aarogya Setu team has worked on a new innovative feature which is called ‘Open API Service’. To help businesses and the economy to start functioning while being safe, the Open API Service enables organizations to check the status of Aarogya Setu and integrate it into its various Work from Home features. The Open API Service of Aarogya Setu addresses the fear/risk of Covid-19 infections and help the people, businesses, and the economy to return to normalcy.
- Aarogya Setu has been powering India’s fight against COVID-19 since its launch on 2nd April 2020. Aarogya Setu has now emerged as the most downloaded contact tracing App in the world, with more than 15 crore users. The overwhelming support of the people has enabled Aarogya Setu to aid the efforts of frontline health workers and the Government in COVID-19 mitigation and management efforts. More than 6.6 million Bluetooth contacts have been traced and the percentage positive of those who have tested is almost 27%. Thus Aarogya Setu based Bluetooth contact tracing and testing are very efficient and effective. Similarly, many others have been advised for caution and quarantine and it has led to breaking the chain of spread and has been effective in early detection and ensuring that fatality rates in India are amongst the lowest. The Aarogya Setu ITIHAS interface which uses location data and Aarogya Setu analytics to predict emerging hotspots at Sub Pincode levels has been very effective in helping the health officials and administration to take necessary precautionary steps. More than 30,000 hotspots have been identified at a very granular level of 300 m X 300 m and shared with State Governments and Districts.
- Since its launch, Aarogya Setu has continuously innovated and introduced more novel features like e-pass integration, QR Code scanning, sharing of Health status with family/known persons - all of which have been very effective in keeping India and Indians safe in line with the motto of Aarogya Setu – Main Surakshit, Hum Surakshit, Bharat Surakshit.
Open API Service
- The Open API Service of Aarogya Setu can be availed by organizations and business entities, who are registered in India with more than 50 employees, and they can use the Open API Service to query the Aarogya Setu Application in real-time and get the health status of their employees or any other Aarogya Setu User, who have provided their consent for sharing their health status with the organization. The Open API shall only provide the Aarogya Setu status and name of the Aarogya Setu User (with User's consent). No other personal data shall be provided through the API.
Source:
PIB
5) Weakening Pakistan-Saudi Arabia Relations
- Recently, a delegation led by Pakistan Army Chief visited Saudi Arabia but was denied a meeting with Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman (MBS).
- It highlights the rift between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia in general and specifically over the issue of Jammu and Kashmir.
Saudi’s Changing Perspective on India:
- Saudi’s increasing friendly and supportive nature towards India has been a gradual process under Crown Prince MBS because he wants to diversify Saudi’s heavily oil-dependent economy and sees India as a valuable partner in the region.
- Saudi Arabia is India’s fourth-largest trade partner (after China, the USA, and Japan) and a major source of energy.
- India imports around 18% of its crude oil requirement from Saudi Arabia which is also a major source of LPG for India.
- With India stopping oil imports from Iran due to the threat of sanctions by the USA, the importance of Saudi Arabia increases even more.
Increasing China Factor:
- Pakistan and China call themselves “all-weather allies” and “iron brothers”.
- China has supported Pakistan on the Kashmir issue, raising it at the United Nations Security Council thrice, over the last year.
- China has also emerged as Pakistan’s biggest benefactor through its funding of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- Originally valued at USD 46 billion, China’s commitment to Pakistan now stands at USD 62 billion.
- Saudi Arabia has also invested in CPEC projects, to the tune of USD 10 billion but Pakistan now seems more interested in Beijing for both diplomatic and economic support.
- Pakistani leaders’ visits to China play an important role in further strengthening the Pakistan-China All-Weather Strategic Cooperative Partnership.
Implications for India:
- India has favored and supported the Arab world and has worked the diplomatic levers through high-level visits and open opportunities for investment and business.
- India has been closely noticing the developments between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia but has not said anything publicly.
- Saudi’s silence on the issues of Jammu and Kashmir and the CAA-NRC has also emboldened India.
- Closer ties between China and Pakistan are worrying for India, especially during the ongoing standoff but with Saudi Arabia’s support, India may have leverage over Pakistan.
History of Cooperation and Support:
- The relationship was most prominent during the 1971 war between India and Pakistan when Saudi Arabia is also reported to have transferred arms and equipment to Pakistan.
- Saudi held that Indian actions were “treacherous and contrary to all international covenants and human values” and found no justification for the Indian aggression except “India’s desire to dismember Pakistan and tarnish its Islamic creed”.
- Post-war, Saudi Arabia consistently supported the call for the return of Pakistan’s prisoners of war and for dropping the Dhaka Trial against them. It also gave loans to Pakistan enabling it to buy arms worth about USD 1 million by 1977.
- Saudi oil and dollars have kept Pakistan’s economy afloat after sanctions following the nuclear tests.
- Saudi has provided oil on deferred payments to Pakistan whenever it ran into economic difficulty.
- Saudi’s funding of madrasas has led to their growth and spread which in turn has given rise to religious extremism.
- In 1990, Pakistan sent its ground forces to defend Saudi Arabia against Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait.
Emerging Differences:
- Pakistan lobbied with the Organisation of Islamic Conference (OIC) for criticizing the Indian move of revoking Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir but statements by Saudi Arabia and the UAE were not harshly critical of India.
- Pakistan has tried to rouse the sentiments among the Islamic countries, but only Turkey and Malaysia have publicly criticized India.
- The alignment over Kashmir at the OIC crystallized since 1990 when the insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir began and since then, it has regularly issued statements on the issue.
- Pakistan has accused Saudi of failing to deliver on the Kashmir cause and OIC for not playing a leadership role in backing Pakistan against India.
- In 2015, Pakistan’s Parliament decided not to support the Saudi military effort to restore an internationally recognized government in Yemen.
- In February 2019 after the Pulwama terror attack, Saudi Arabia and the UAE, along with the USA, put in efforts on the release of the Indian Wing Commander Abhinandan who was captured by Pakistan.
- Saudi Arabia angered by Pakistan’s accusations demanded the return of the USD 3 billion loans and refused to sell oil on deferred payment. Pakistan immediately returned USD 1 billion, displaying the rift.
- In November 2018, Saudi announced a USD 6.2 billion loan package for Pakistan which included USD 3 billion in loans and an oil credit facility amounting to USD 3.2 billion.
- Pakistan is unable to pay the next tranche which seems difficult given the current economic situation and to make things worse, Saudi has refused to take part in Pakistan’s patch-up exercise.
- Pakistan’s efforts to please Turkey and Malaysia have also angered Saudi Arabia because Turkey has been trying to position itself as the new leader of the Muslim world, challenging Saudi Arabia’s long-held position.
Way Forward
- Saudi Arabia does not want conflict and regional instability and it has made it clear that it values economic opportunities, which is why it is not involving in the Kashmir issue in India or the terrorism issue in Pakistan.
- For India, it is important that the Pakistan-China and the Pakistan-Saudi axes are not fused together at the moment and it is not a Saudi-Pakistan-China triangle. The rest of it and the future of these layered relations depends on how India leverages the situation.
Source:
Indian Express
6) Chora Museum and New Gas Field: Turkey
Recently, the Turkish President reconverted the Chora museum into a mosque.
This is the second museum after Hagia Sophia to be converted into a mosque.
Turkey has also found a new gas field in the Black Sea.
Chora Museum:
- It was built initially as a church in 534 AD, during the early Byzantine period.
- In the 11th century, its internal walls, pillars, and domes were covered with mosaics and frescoes showing scenes from biblical stories.
- After the conquest of Constantinople (the capital city of the Roman Empire) by the Ottomans (1453), the church was seized and turned into a mosque in 1511.
- In 1945, it was converted into a museum.
- Chora is also known as Kariye in Turkish and the medieval Church of the Holy Saviour in Chora.
Reason:
- The reconversion can be seen as the Turkish President’s pro-Islamic policies, where he emphasizes Turkey’s Ottoman history and domestic achievements over Western ideas and influences.
- By adopting pro Islamic policies the Turkish President aims to become the leader of the Muslim world.
- The Turkish President has also taken anti-India positions, especially on Kashmir to bolster its own position in the Muslim world.
- It can also be seen as a counter to the USA’s recognition of Jerusalem as the capital of Israel.
- Jerusalem which has a significant population of Arab-Muslims who are becoming more and more hostile because of the USA's recent stand on Israel-Palestine issue. This step of conversion of mosques would gain the support of Arab countries for Turkey.
Gas Field in the Black Sea:
- Recently, Turkey has found its biggest ever (a 320 billion cubic meter) natural gas field discovery in the Black Sea. The gas field will become functional in 2023.
- Turkey is determined to become a net energy exporter. The discovery has the potential to transform Turkey’s dependence on Russia, Iran, and Azerbaijan for energy imports.
- Currently, Turkey is having a chronic current account deficit, any reduction in Turkey’s energy import bill would boost its finances. It will also help the Lira (Currency of Turkey) to recover against the dollar.
- Currently, Turkey is also having strained relations with its neighbor Greece over the exploration of natural resources in the Mediterranean sea.
Source:
Indian Express
7) New Constitution of Sri Lanka
- The Sri Lankan President Gotabaya Rajapaksa (elected in 2019), while addressing the inaugural session of the Parliament, said that Sri Lanka will draft a new constitution and abolish the 19th Amendment that curtailed the powers of the President and strengthened the role of Parliament.
- Sri Lanka’s new Cabinet includes members from the Rajapaksa family.
- Mahinda Rajapaksha is the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka.
- The Rajapaksa led Sri Lanka People’s Party (SLPP) won a landslide victory in the recently held parliamentary elections (August 2020), allowing the influential family to consolidate power for the next five years.
19th Amendment:
- It was passed in 2015 during the former President Maithripala Sirisena-Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe’s term (2015-19).
- It sought not only to clip the President’s executive powers but also to strengthen the independence of key pillars such as the judiciary, public service, and elections.
- It brought back the two-term limit on the Presidency.
- It was hailed by many, including members of civil society, as progressive legislation in contemporary Sri Lankan history, even as its critics found it falling short in some respects.
- However, the Rajapaksa camp viewed its clauses as primarily intended to prevent its leaders’ return to power.
- It prevented dual citizens from contesting elections. At the time, two of the Rajapaksa family members including the current president were dual citizens of the USA and Sri Lanka.
- Its abolishment will strengthen Rajapaksa's grip on power because the country will return to its previous constitutional status, in which the President could appoint officials for the police, judiciary, and public service and dissolve Parliament anytime after one year.
New Constitution:
- The President said that the new Constitution would prioritize the concept of “one country, one law for all the people.”
- Sri Lanka's constitution has been changed 19 times since 1978, creating a lot of uncertainties and confusion.
- Changes will be made to ensure the stability of Parliament and people’s direct representation while retaining the salutary aspects of the proportional representation system.
- Rights activists see the planned changes to the Constitution as an attempt to further empower the SLPP and the Rajpaksha brothers’ mainly Buddhist - Sinhalese speaking electorate.
- The Rajapaksa family, which dominated the government from 2005 to 2015, witnessed the climax of the country’s long civil war (1983-2009).
- The war divided Sri Lanka along ethnic lines - pitting the majority Buddhist Sinhalese-dominated government against Tamil rebels who wanted a separate state.
- The rebels were defeated by government forces in 2009.
Way Forward
- For Sri Lanka, the Constitution-making process of the new Government shall strengthen Sri Lanka’s democracy and provide an inclusive platform for the country to achieve prosperity for all.
- For India, it should push for the reconciliation efforts for the Tamils in Sri Lanka while remaining sensitive to Sri Lanka’s security concerns.
Source:
The Hindu
8) Election Commissioner
The Centre has appointed Rajiv Kumar as the Election Commissioner. He has been
appointed in place of Ashok Lavasa, who has resigned to join the Asian
Development Bank (ADB).
Constitutional Provisions:
- The Election Commission of India is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India. The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country (Article 324).
- It is not concerned with the elections to panchayats and municipalities in the states. For this, the Constitution of India provides for a separate State Election Commission.
- The Election Commission shall consist of the chief election commissioner and a such number of other election commissioners, if any, as the President may from time to time fix.
- Presently, it consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners.
Appointment & Tenure of Commissioners:
- The President appoints Chief Election Commissioner and Election Commissioners.
- They have tenure of six years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- They enjoy the same status and receive salary and perks as available to Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
- All Election Commissioners have equal say in the decision making of the Commission.
Removal:
- They can resign anytime or can also be removed before the expiry of their term.
- The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from his office in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- In other words, he can be removed by the President based on a resolution passed to that effect by both the Houses of Parliament with a special majority, either on the ground of proved misbehavior or incapacity.
- Thus, he does not hold his office until the pleasure of the President, though he is appointed by him.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the chief election commissioner.
Limitations:
- The Constitution has not prescribed the qualifications (legal, educational, administrative, or judicial) of the members of the Election Commission.
- The Constitution has not specified the term of the members of the Election Commission.
- The Constitution has not debarred the retiring election commissioners from any further appointment by the government.
Powers and Functions of the Election Commission
- Administrative:
- To determine the territorial areas of the electoral constituencies throughout the country based on the Delimitation Commission Act of Parliament.
- To prepare and periodically revise electoral rolls and to register all eligible voters.
- To grant recognition to political parties and allot election symbols to them.
- Election Commission ensures a level playing field for the political parties in election fray, through strict observance by them of a Model Code of Conduct evolved with the consensus of political parties.
- Advisory Jurisdiction & Quasi-Judicial Functions:
- Under the Constitution, the Commission has advisory jurisdiction in the matter of post-election disqualification of sitting members of Parliament and State Legislatures.
- The opinion of the Commission in all such matters is binding on the President or, as the case may be, the Governor to whom such opinion is tendered.
- Further, the cases of persons found guilty of corrupt practices at elections that come before the Supreme Court and High Courts are also referred to the Commission for its opinion on the question as to whether such person shall be disqualified and, if so, for what period.
- The Commission has the power to disqualify a candidate who has failed to lodge an account of his election expenses within the time and in the manner prescribed by law.
Source:
The Hindu
9) RBI at end of ratecut cycle
- The Reserve Bank is at the end of its ratecut cycle as inflation is unlikely to decline materially from the current level, and the onus of economic recovery has now shifted to the government
- Where high inflation was cited as the prime reason for the unanimous decision to hold rates
- To push economic growth, but surprised many by holding rates at the August review as inflation overshot its target.
- Fiscal policy should play a decisive role if we have to nurture any hopes of a fastpaced recovery
- We now believe that we are at the end of the rate-cut cycle and expectations of large rate cuts must be anchored as inflation is unlikely to decline materially from the current level
- Hinting at best there can be a 0.25% more of rate cuts in the offing
- The economists said they feel inflation — which came at 6.9% for July — could be sticky because their estimates show the large procurement by the government may have resulted in 0.35-0.40% upward impact.
Let us understand a few points of the news but before that one concept:
- Nominal Interest rate = Inflation + Real Interest Rate
- This formula is for anyone and not specific to depositors only. It is for RBI, banks, people, borrowers anyone.
- Nominal means something which u get/pay in CURRENCY terms. For example, you deposited Rs. 100 in a bank at an interest rate of 8%. So, every year you will get RUPEEs 8 as interest from the bank in the form of Rupee/Currency. So, this Rs 8 ( or 8%) is called nominal interest rate but if inflation is 7% then basically u benefitted just 1% i.e. your actual return is just one percent which is called real interest rate (or real return).
- For example, I borrowed money from the bank at 9% interest. Then this 9% I will be paying every year to the bank in currency terms, so this 9% is the nominal interest rate. But if inflation is also 9% then it means I am not paying any real interest to the bank. The rupee is losing value by 9% every year (inflation 9%) and I am paying 9% interest every year, so I am not paying anything extra (real) to the bank. And I will say that my real cost of borrowing is 0%.
Now the NEWS:
- Monthly inflation is hovering around 6% (just for July it was 6.9%). Since RBI reduced the repo rate (to push for economic growth), reverse repo rate got reduced and deposit and lending rate also got reduced. Now the deposit rates in banks have come down below 6% (most of the banks are giving between 5% to 5.5%). This is creating a problem. If u deposit money in the bank at 5.5% and inflation is 6%.............then basically you are losing money (real interest rate becomes negative of -0.5%). This is leading to people moving their deposits from banks to SHARE MARKETs which is rising like anything (not at all in sync with the economic reality, there is another news in HINDU, the image shared below). The fear in the minds of the people, because COVID is not leading to increased purchase of goods and services and demand, is not picking up even from those people who have money. When the demand is not picking up..............businessmen are not willing to invest even if the REAL cost of borrowing for them is almost negligible (borrowing rate 7% and inflation 6.9%, SO real interest rate = 7% - 6.9% = 0.1%).
- All this is leading to an unrealistic boom in the stock market and which may crash in the future because it is not supported by actual real economic activity on the ground. The Indian stock market is also booming because more foreign money is coming in (sufficient foreign liquidity) and hence our FOREX is also increasing.
- SO, RBI has said that NOW it has reached at the end of the repo rate cut (cycle) and it cannot further reduce it beyond 4%. (REPO RATE CUT SHOULD BE IN SYNC WITH INFLATION. RBI SHOULD CUT THE REPO RATE ONLY WHEN THE INFLATION IS COMING DOWN OTHERWISE IT WILL LEAD TO A LOT OF PROBLEMS EXPLAINED ABOVE)
- So, now the ball is in Govt's court and it should focus on its FISCAL POLICY (fiscal means related to govt expenditure and tax policy). When govt will spend more may be on the construction of infrastructure then money will directly reach the public and economic growth may be revived.
There are two terms used in the last column, its meanings in the context of today's news are:
- ANCHORED: Stopped
- STICKY: Not going to change
Source:
The Hindu
10) Dragonfly Festival
- The first-ever State Dragonfly Festival, also known as Thumbimahotsavam 2020 will be organized in Kerala jointly by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF)-India State unit and Society for Odonate Studies (SOS).
- It will be the part of National Dragonfly Festival being organized by the WWF India, Bombay Natural History Society & Indian Dragonfly Society,
- The third edition of the National Dragonfly Festival was organized online in August 2020.
- It aims at building awareness about the importance of dragonflies and damselflies and the need to conserve them.
- Dragonflies act as important bio-indicators of the ecological health of an area.
- The festival will consist of training resource persons, webinars, and competitions.
- The festival will also provide an opportunity for people to undertake citizen science projects in their backyards during Covid-19 restrictions.
- Some specific target groups for this festival include zoology teachers, members of biodiversity management committees, eco-clubs, the Forest Department, people from ecotourism activities, etc.
Society for Odonate Studies (SOS)
- SOS is a non-political, non-profit organization formed to impart knowledge to the public on the insect order of Odonata (which comprises dragonflies and damselflies) and to conduct scientific studies, with the objective of conservation of the species and their habitats.
Source:
The Hindu



Comments
Post a Comment