Current Affairs Of Today Are
1) Decadal forecast system
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) is planning a ‘decadal forecast’ system along the lines of the United Kingdom’s Met Office to ensure better predictability in the climate time scale, said Dr. M. Rajeevan, Secretary, MoES
- Speaking on the sidelines of the 6th International Conference on Climate Services being held at the Pune-based Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM)
- The system, based on a coupled climate model, would first be taking shape in the form of a research program and would be operational only after its merits had been evaluated.
- This is a new idea with more relevance to present climate forecasting needs. So, given the need for longer-range prediction for 10 or 20 years, we will be starting a new program in the country using a coupled climate model by utilizing signals emanating from deep oceans to predict decadal climate changes
- The system would be explored as a research program to be taken up by IITM along with collaboration from the India Meteorological Department and other entities.
- The World Meteorological Organization has set up global producing centers, coordinated by the U.K. Met Office, for annual to decadal projections that are already providing global-scale information
- Once the system was established, it would initially function for longrange forecasting at the national level and the model, if successful, would later be downscaled to the state or even district-level
- There were several gaps in the understanding of regional climate variability and its connections to global phenomena like Indian Ocean Dipole. Indian forecasters faced a challenge in maintaining the quality of climate observations, and there is a need on the part of researchers to develop applications for specific sectors based on the available climate forecast.
Source: The Hindu
2) ‘Protected Special Agricultural Zone’ (PSAZ)
- Chief Minister Edappadi K. Palaniswami’s announcement that the Cauvery delta region would be declared ‘Protected Special Agricultural Zone’ (PSAZ) may not affect various ongoing projects in the districts, including hydrocarbon exploration. Mr. Palaniswami had said no “new projects such as the hydrocarbon project” would be allowed in delta districts.
- The primary intention of the government is to prohibit any “fresh” attempts at the exploration of gas and minerals in the Cauvery delta region, senior bureaucrats indicated. “This is wetland ecology and such explorations would affect agriculture severely. Moreover, such explorations would also lead to seawater intrusion.”
- Since the ongoing projects in the Cauvery delta have already obtained the necessary permission from the authorities concerned, they may not be affected by the announcement,” informed sources said.
- The proposed ₹50,000 crore investment in Cuddalore by Haldia Petrochemicals would be allowed since “the unit is outside” the Cauvery delta core region. Besides, it is only replacing another private player.
- The Chief Minister has so far not clarified about the fate of the ongoing projects in the region. The proposed PSAZ would cover the entire Nagapattinam, Tiruvarur and Thanjavur districts. The remaining five districts would be covered only partially.
- The declaration was primarily to stop the “local exploitation of underground minerals and gas.” That way, refineries could be allowed since they would only use imported oil
- Though the contours of the policy are yet to be outlined, sources hinted that infrastructure projects such as the laying of roads and railways and construction of bridges would not be affected.
Source: The Hindu
3) “State of the World's Children Report 2019” of UNICEF
- As per UNICEF's State of the World's Children Report 2019, the Under 5 Mortality Rate in India is 37 per 1,000 live births against Global average of 39 per 1,000 live births in 2018, which translates to more than 8 lakhs under 5 deaths in India.
- As per the Sample Registration System (SRS) 2010-13 report of Registrar General of India, major causes of child mortality in India are: Prematurity & low birth weight (29.8%), Pneumonia (17.1%), Diarrheal diseases (8.6%), Other non-communicable diseases (8.3%), Birth asphyxia & birth trauma (8.2%), Injuries (4.6%), Congenital anomalies (4.4%), Ill-defined or cause unknown (4.4%), Acute bacterial sepsis and severe infections (3.6%), Fever of unknown origin (2.5%), All Other Remaining Causes (8.4%).
- As per the UNICEF 2019 report, Globalization, urbanization, inequities, humanitarian crises and climate shocks are driving unprecedented negative changes in the nutrition situation of children around the world.
- The government of India has launched POSHAN (Prime Minister Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment) Abhiyaan, to address malnutrition challenges in India by engaging all the important stakeholders in a convergent approach. The goals of POSHAN Abhiyaan are to prevent and reduce stunting, underweight and low birth weight by 2% per annum and the reduction of anemia by 3% per annum.
- The Government of India has also launched several schemes under the aegis of Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) to tackle malnutrition in the country including Anganwadi Services, Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG) and Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojna (PMMVY) to improve the nutritional and health status of children in the age-group 0-6 years. The Anganwadi Services scheme provides a package of six services i.e. Supplementary Nutrition, Pre School Non-formal Education, Nutrition and Health Education, Immunization, Health checkups, and referral services.
- To address child mortality and morbidity, the Government of India is supporting all States/UTs under National Health Mission in implementation of Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child, Adolescent Health and Nutrition (RMNCAH+N) strategy, which has following interventions:
- Strengthening essential newborn care at all delivery points, the establishment of Sick Newborn Care Units (SNCU), Newborn Stabilization Units (NBSU) and Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC) units for the care of sick and small babies.
- Home Based Newborn Care (HBNC) and Home-Based Care of Young Children (HBYC) by ASHAs to improve child-rearing practices and to identify sick new-born and young children.
- Early initiation and exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months and appropriate Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) practices are promoted under Mothers’ Absolute Affection (MAA) in convergence with the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) is being supported to provide vaccination to children against life-threatening diseases such as Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Polio, Tetanus, Hepatitis B, Measles, Rubella, Pneumonia and Meningitis caused by Haemophilus Influenzae B. The Rotavirus vaccination has also been rolled out in the country for prevention of Rota-viral diarrhea. Mission Indradhanush is targeted to immunize children who are either unvaccinated or partially vaccinated i.e. those that have not been covered during the rounds of routine immunization for various reasons. Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) 2.0 is rolled-out as per road-map for achieving 90% full immunization coverage across the country.
- Nutrition Rehabilitation Centres (NRCs) have been set up at public health facilities to treat and manage children with Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) admitted with medical complications.
- Defeat Diarrhoea (D2) initiative has been launched for promoting ORS and Zinc use and eliminating the diarrhoeal deaths by 2025.
- Social Awareness and Actions to Neutralize Pneumonia Successfully (SAANS) initiative for reduction of Childhood morbidity and mortality due to Pneumonia.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) strategy as a part of Poshan Abhiyan aims to strengthen the existing mechanisms and foster newer strategies to tackle anemia, which include testing & treatment of anemia in school-going adolescents & pregnant women, addressing non-nutritional causes of anemia and a comprehensive communication strategy. National Deworming Day (NDD) is implemented bi-annually every year for the deworming of children (one to nineteen years of age).
- All the children from 0 to 18 years of age are screened for 30 health conditions classified into 4Ds - Diseases, Deficiencies, Defects and Developmental delay under “Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakaram” (RBSK) to improve the quality of survival and to reduce out of pocket expenditure of families. District early intervention centers (DEIC) at the district health facility level are established for confirmation and management of the 4D’s.
- Village Health Sanitation and Nutrition Days (VHSNDs) are observed for the provision of maternal and child health services and awareness on maternal and child health and nutrition education through mass and social media to improve health practices and to generate demand for service uptake.
- Name-based tracking of mothers and children till two years of age is done through the RCH portal to ensure complete antenatal, intranasal, postnatal care and immunization as per schedule.
- Promotion of Institutional deliveries through cash incentive under Janani SurakshaYojana (JSY) and Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) which entitles all pregnant women delivering in public health institutions to absolutely free delivery including Caesarean section, post-natal care and treatment of sick infants up to one year of age. Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) is another maternity benefits program under which cash incentive is provided to pregnant women and lactating mothers.
4) Infiltration on Indo-Bangladesh border
- Union Minister of State for Home Affairs, Shri Nityanand Rai, in a written reply in Lok Sabha to a question regarding detection, arrest, and deportation of illegal infiltrators on Indo-Bangladesh border said that the Government has adopted a multi-pronged approach which inter-alia includes round the clock surveillance and patrolling on the borders and establishment of observation post; construction of border fencing & floodlighting; introduction of modern and Hi-Tech surveillance equipment; up-gradation of intelligence setup and enhanced coordination with the State Governments and concerned intelligence agencies.
- Technological solutions are being used for vulnerable areas where physical fencing is not feasible, on a pilot basis to begin with, on Indo-Pakistan Border and Indo-Bangladesh Border. The technological solutions are based on the integration of sensors and surveillance equipment like radars, day and night vision cameras, etc in a network architecture with command and control system.
Source: PIB
5) Workshop on Van Dhan and Entrepreneurship Development
- Union Minister for Tribal Affairs Shri Arjun Munda inaugurated the “Workshop on Van Dhan and Entrepreneurship Development” organized by TRIFED under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana (PMVDY) is an initiative targeting livelihoods generation for tribals by harnessing the wealth of the forest i.e., Van Dhan. The program aims to tap the traditional knowledge and skills of tribals and add branding, packaging and marketing skills to optimize their income through a market-led enterprise model by setting up Van Dhan Kendras (VDVKs). The objective of PMVDY is to create tribal enterprise comprising of tribal gatherers/ entrepreneurs, who would collectively undertake all related activities starting from the collection of NTFPs through sustainable harvesting, value-addition, packaging, branding, and marketing of value-added products. He informed the Members that PMVDY envisages the creation of tribal enterprises for employment and entrepreneurship development of 45 Lakh tribals, involving 1 Lakh SHGs/5000 VDVKs covering 27 States and 307 districts during the next 3 years.
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Govt of India through TRIFED started the above initiative in Aug. 2019. TRIFED has so far sanctioned proposals for the establishment of 1101 Van Dhan Kendras in 26 States and 1 UT. The scheme is being implemented through State Nodal Departments and State/District Implementing Agencies. Reputed Institutions like IITs, IIMs and National Level Intuitions have been associated with supporting this initiative by taking their help in devising the training module and imparting training to members of Van Dhan Kendras on various aspects including the processing of forest products, branding, packaging, and marketing of value-added products. These reputed institutions will continue their support post-training to the members for developing a Van Dhan enterprise. Besides, Organisations like FICCI, CII, ASSOCHAM, PHD chamber, DICCI, etc. are also being associated with bringing support and participation of trade and industry in this Van Dhan program. TRIFED has reached out to various Ministries like Commerce, MSME, RD, Railways, etc also for support to promote tribal products through a multi-pronged strategy.
- The process of establishment of Van Dhan Kendras has gained momentum in the States. Out of sanctioned 1101 Van Dhan Kendras, 406 Van Dhan Kendras have identified tribal beneficiaries, 174 have done the training of SHGs/VDVKs and 41 Kendras have initiated the process of value-addition and processing operations.
Source: The Hindu
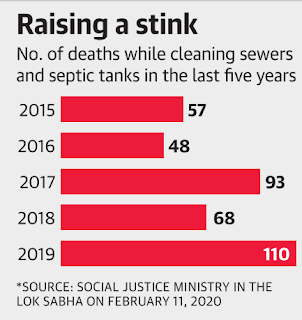
6) National survey Cleaning of drains & septic tanks deaths
- The number of people who died while cleaning sewers and septic tanks in the country increased by almost 62% from 68 in 2018 to 110 in 2019, according to a reply was given by the Social Justice and Empowerment (SJE) Ministry to the Lok Sabha
- SJE Minister of State Ramdas Athawale replied to the question asked by Bharatiya Janata Party MPs Anil Firojiya, Mohanbhai Kalyanjibhai Kundariya and Lallu Singh about the incidents of manual scavenging, which is banned under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013
- The reply said a total of 14,559 manual scavengers had been identified by Municipalities and Gram Panchayats in 13 States from 2013-2014 till January 31, 2020. Apart from that, a national survey was conducted in 194 districts in 18 States where 48,345 manual scavengers were identified till January 31, taking the total to 62,904.
- National Commission for Safai Karamcharis had received reports about the death of people cleaning sewers and septic tanks
- These cases were reported from 18 States and Union Territories, while 13 States and UTs submitted “nil reports”.
Source: The Hindu
7) Steps Taken by the Ministry of Home Affairs for Police Modernization
- Union Minister of State for Home Affairs, Shri G Kishan Reddy, in a written reply in Lok Sabha to a question regarding modernization of police forces, said that this is a continuous and ongoing process. While ‘Police’ and ‘Public Order’ are State Subject as per Schedule VII to the constitution of India, to supplement the efforts of the States for equipping and modernizing of their police forces, under the scheme of ‘Assistance to States for Modernisation of Police’ {erstwhile scheme of Modernisation of Police Force (MPF)}, the States have been provided central assistance for training gadgets, advanced communication, police buildings, police housing, mobility, and forensic equipment, etc. as per the proposals of the State Governments by their strategic priorities and requirements.
- The Union Government has created an all India digital network –Crime & Criminal Tracking Networking System (CCTNS) in 15152 out of 15985 police stations of the country which has digitized police processes like registering complaints, FIRs, Investigation details, etc. 100% FIRs are being recorded in 14,992 police stations. Also, the Government has launched the Interoperable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) which integrates the process of speedy justice by facilitating data exchange between the courts, police, prosecution, jails and the forensic laboratories.
- To achieve the objectives of completion of police investigation within two months of filing FIR by police for sexual assaults, the Government has facilitated the monitoring of timelines in police investigation through the Investigation Tracking System for Sexual Offences (ITSSO) Portal, using CCTNS data. ITSSO is available to law enforcement agencies and gives details on pending cases. The Government has also launched a National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO) for law enforcement officers. NDSO allows tracking of repeat and habitual sex offenders as well as initiate preventive measures against sexual offenses. A cybercrime portal is also functional.
Source: PIB
8) WHO Names Disease Caused by New Coronavirus: COVID-19
- WHO locks down a naming convention for the disease caused by novel coronaviruses. As for the virus itself (2019-nCoV), the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses has named it SARS-CoV-2.
- There is now an official name for the disease caused by the new coronavirus, which has claimed more than 1000 lives: COVID-19
- an 11-member committee from the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) has assigned a name for the virus that causes the disease now known as COVID-19. The name they have put forth is SARS-CoV-2, which “formally recognizes this virus as a sister to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses.”
- The ICTV is concerned with the designation and naming of virus taxa (i.e. species, genus, family, etc.) rather than the designation of virus common names or disease names. For an outbreak of a new viral disease, there are three names to be decided: the disease, the virus, and the species. The World Health Organization (WHO) is responsible for the first, expert virologists for the second, the ICTV for the third.
- The WHO issued guidelines in 2015 for naming new human infectious diseases and syndromes which called for avoidance of geographic locations (e.g. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, Spanish Flu, Rift Valley fever), people’s names (e.g. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Chagas disease), species of animal or food (e.g. swine flu, bird flu, monkeypox), cultural, population, industry or occupational references (e.g. legionnaires), and terms that incite undue fear (e.g. unknown, fatal, epidemic).
- The best practices also state that a disease name should consist of generic descriptive terms, based on the symptoms that the disease causes (e.g. respiratory disease, neurologic syndrome, watery diarrhea) and more specific descriptive terms when robust information is available on how the disease manifests, who it affects, its severity or seasonality (e.g. progressive, juvenile, severe, winter). If the pathogen that causes the disease is known, it should be part of the disease name (e.g. coronavirus, influenza virus, salmonella).
Source: Global Bio Defence


Comments
Post a Comment