Current Affairs Of Today
1) Restoration of coral reefs in Gulf of Kutch
The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), with help from Gujarat’s Forest Department, is attempting for the first time a process to restore coral reefs using bio rock or mineral accretion technology. A bio rock structure was installed one nautical mile off the Mithapur coast in the Gulf of Kutch
What is Bio Rock?
- Biorock is the name given to the substance formed by electro accumulation of minerals dissolved in seawater on steel structures that are lowered onto the sea bed and are connected to a power source, in this case, solar panels that float on the surface
- The technology works by passing a small amount of electrical current through electrodes in the water
- When a positively charged anode and negatively charged cathode are placed on the seafloor, with an electric current flowing between them, calcium ions combine with carbonate ions and adhere to the structure (cathode). This results in calcium carbonate formation. Coral larvae adhere to the CaCO3 and grow quickly as fragments of broken corals are tied to the bio rock structure, where they can grow at least four to six times faster than their actual growth as they need not spend their energy in building their own calcium carbonate skeletons.
Other Coral Reefs Restoration
 |
| Acroporidae |
In 2015, the same group of ZSI scientists with the support of the Gujarat Forest Department had successfully restored branching coral species (staghorn corals) belonging to the family Acroporidae (Acropora Formosa, Acropora humilis, Montipora Digitata) that had gone extinct about 10,000 years ago to the Gulf of Kutch. The researchers claimed that the specimens for regenerating these corals were brought from the Gulf of Mannar with the help of Tamil Nadu’s Forest Department.
 |
| staghorn corals |
The degradation of coral reefs across the world and also in India threats were posed both by climate changeinduced acidification as well as by anthropogenic factors. Observing that coral reefs were the most diverse ecosystem on the earth, India has four major coral reefs areas: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Gulf of Mannar and the Gulf of Kutch
2) MGNREGA scheme
- The Centre is on the verge of running out of funds for the crucial Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) scheme.
- More than 96% of the allocated money has already been spent or is needed to pay pending dues, with less than ₹2,500 crores left to sustain the scheme for the next two months
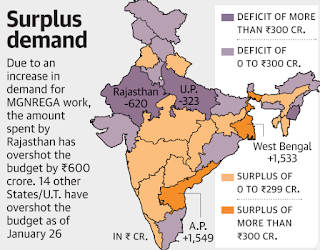
- Fifteen states are already in the red. According to the scheme’s financial statement as on January 26, Rajasthan has the highest negative net balance of ₹620 crores, followed by ₹323 crores in Uttar Pradesh.
- The situation on the ground may be worse as States do not always enter pending payments into the information system. “January, February, and March are months with little agricultural activity when rural workers desperately need employment. However, the scheme is running out of money and will enter next year with pending liabilities
- Several economists have recommended that putting money into the hands of rural consumers via MGNREGA is key to kickstarting the economy. However, this year’s budget allocation was ₹60,000 crore, lower than the amount spent in the previous year
3) India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) project
- Villagers in different parts of Tamil Nadu used gram sabha meetings, organized on Republic Day, to pass resolutions against initiatives such as the hydrocarbon exploration and Indiabased Neutrino Observatory (INO) projects, which, they feared, would be detrimental to their respective regions
- Arguing that the hydrocarbon exploration project, for which the Union government recently did away with the need to obtain environmental clearance and hold public consultations, would adversely affect the fertile agricultural belt, several panchayats in Pudukottai, Thanjavur and Tiruvarur districts adopted resolutions at the gram sabha meetings.
- Acknowledging that a resolution against the implementation of hydrocarbon project was adopted at Neduvasal Kizhakku panchayat
- A resolution was adopted to the effect that the project should not be implemented in fertile areas in Pudukottai district.
4) India helps Maldives tackle measles outbreak
- India has stepped in to help the Maldives tackle a recent outbreak of measles. The Indian Embassy in Male recently handed over 30,000 doses of measles and rubella (MR) vaccine to the Maldivian Health Ministry.
- The outbreak comes less than three years after the World Health Organisation declared the Maldives measles-free.
Background
- The Indian government’s initiative comes even as the two countries implement the Memorandum of Understanding on Health cooperation — signed during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Male in June 2019.
- Secretary-level delegations met in Male early January to draw a roadmap for cooperation, in capacity building and training of doctors and medical professionals, disease surveillance, training of mental health professionals, setting up of digital health capacities in the Maldives.
About Measles
- Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It remains an important cause of death among young children globally, despite the availability of a safe and effective vaccine.
- Spread: Measles is transmitted via droplets from the nose, mouth or throat of infected persons.
- Initial symptoms, which usually appear 10–12 days after infection, include high fever, a runny nose, bloodshot eyes, and tiny white spots on the inside of the mouth. Several days later, a rash develops, starting on the face and upper neck and gradually spreading downwards.
- Vulnerability: Severe measles is more likely among poorly nourished young children, especially those with insufficient vitamin A, or whose immune systems have been weakened by HIV/AIDS or other diseases.
- The most serious complications include blindness, encephalitis (an infection that causes brain swelling), severe diarrhea and related dehydration, and severe respiratory infections such as pneumonia.
- Prevention: Routine measles vaccination for children, combined with mass immunization campaigns in countries with low routine coverage, are key public health strategies to reduce global measles deaths.
- Preventive efforts: Under the Global Vaccine Action Plan, measles and rubella are targeted for elimination in five WHO Regions by 2020. WHO is the lead technical agency responsible for the coordination of immunization and surveillance activities supporting all countries to achieve this goal.
What is Rubella?
Also called German Measles, Rubella is a contagious, generally mild viral infection that occurs most often in children and young adults.
5) NavIC Qualcomm
Qualcomm Technologies has unveiled mobile chipsets supporting the Indian regional satellite navigation system – NavIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation).
Significance
The release of chipsets will help accelerate the adoption of NavIC by smartphone Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). The OEMs can now release any new models for the Indian market which are NavIC enabled, thus eventually making NavIC as a standard feature in the upcoming handsets, applications, processors, etc.
What is NAVIC?
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) is an independent regional navigation satellite system designed to provide position information in the Indian region and 1500 km around the Indian mainland.
Services provided:
IRNSS would provide two types of services, namely Standard Positioning Services available to all users and Restricted Services provided to authorized users.
Its applications include:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation.
- Disaster Management.
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management.
- Integration with mobile phones.
- Precise Timing.
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture.
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travelers.
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers.
How many satellites does NAVIC consist of?
It is a regional system and so its constellation will consist of seven satellites.
Three of these will be geostationary over the Indian Ocean, i.e., they will appear to be stationary in the sky over the region, and four will be geosynchronous – appearing at the same point in the sky at the same time every day.
This configuration ensures each satellite is being tracked by at least one of fourteen ground stations at any given point of time, with a high chance of most of them being visible from any point in India.
Why it is necessary to have an indigenous global navigation system?
Having a global navigation system bolsters the ability of a nation to serve as a net security provider, especially through the guarantee of such assurance policies. It can also play a significant role in relief efforts post disasters such as the tsunami in the Indian Ocean region in 2004 and the Pakistan-India earthquake in 2005.
6) Kangaroo mother care (KMC)
- Kangaroo mother care (KMC) or the intervention where babies are placed in skintoskin contact with their mothers and exclusively breastfed has been recommended worldwide for stable low-birthweight newborns. Stable babies are defined as babies who do not need respiratory support or intravenous fluids and can accept oral feeds. Though previous studies have shown that keeping the baby in contact with the mother improves survival in babies (less than 2 kg weight at birth) when compared to standard hospital care, global data show that barely 5% receive such care. Also, there is no such evidence on kangaroo mother care impact when initiated at homes in India
- Kangaroo mother care improved survival by 30% and 25%, in babies until 28 days and six months of age, respectively. The paper adds that such care for all infants with low birthweight could substantially reduce neonatal and infant mortality.
- About 97% of the world’s lowweight babies are born in developing countries, and India accounts for about 40% of this, implying an urgent need for effective interventions.
- For the study, over 8,000 stable lowbirthweight babies weighing less than 2.25 kg, were enrolled from two districts in Haryana, during 2015-2018 and randomly assigned to intervention and control groups. Kangaroo mother care intervention was initiated at home, at an average age of 33 hours and delivered during the first month of life, through home visits. The enrolled babies were followed up at one, three and six months of age.
7) ICJ ruling on Rohingya crisis
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has given its verdict on the Rohingya crisis.
- The ruling of the court is binding on Myanmar, and cannot be appealed.
- However, no means are available to the court to enforce it.
What the ruling says?- provisional measures
- The government of Myanmar should immediately take “all measures within its power” to prevent atrocities against members of the minority Rohingya Muslim community.
- This is to be done following its obligations under the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide.
- Myanmar shall ensure that its military or any irregular armed units within its control, do not commit any of the acts described above, or conspire to commit, direct, attempt to commit, or be complicit in genocide.
- Myanmar shall take “effective measures to prevent the destruction and ensure the preservation of evidence related to allegations of acts” of genocide.
How the case reached ICJ?
- It was the Republic of the Gambia. It went to the ICJ in November 2019, accusing Myanmar of genocide, which is the most serious of all international crimes.
- The Gambia was backed by the 57-member Organisation for Islamic Cooperation (OIC).
- Myanmar was represented by Nobel Laureate Aung San Suu Kyi.
What Next?
- This order is a provisional measure and a restraining order.
- The hearings dealing with the main, and more serious allegations of genocide by the Myanmar military, have not even started. And cases at the ICJ often drag on for years on end, and no quick closure can be reasonably expected.
How common is it to convict a country for genocide?
- So far, only three cases of genocide worldwide have been recognized since World War II: Cambodia (the late 1970s), Rwanda (1994), and Srebrenica, Bosnia (1995).
- Proving genocide has been difficult because of the high bar set by its ‘intent requirement’ — that is showing the genocidal acts were carried out with the specific intent to eliminate a people based on their ethnicity.
Rohingya Crisis in Short
- An estimated 7.3 lakh Rohingya have fled to Bangladesh since 2017 when the Myanmar military launched a brutal crackdown on Rohingya villages in the country’s coastal Rakhine state. In August 2019, the UN said the army’s action was carried out with “genocidal intent”.
- Myanmar has stoutly denied all allegations of genocide. It has also denied nearly all allegations made by the Rohingya of mass rape, killings, and arson against its army. Myanmar says the soldiers carried out legitimate counterterrorism operations.
8) Ophichthus kailashchandrai
- This is a new snake eel species residing in the Bay of Bengal. It was discovered recently.
- It has been named Ophichthus kailashchandrai to honor the vast contributions of Dr. Kailash Chandra, Director of ZSI, to Indian animal taxonomy.
- It is the eighth species of the Ophichthus genus found on the Indian coast.
- Lives at a depth of around 50 meters in the sea.
- Individuals of this species are around 420 mm to 462 mm in length.
- They are light brown in color, with white fins.
- It feeds on small fish and crabs. The outer surface of their bodies is slimy but they are not poisonous.
9) Web portal ‘GATI’
- Launched by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
- Created by NHAI.
- The portal ‘GATI’ can be accessed from NHAI’s website, and contractors and concessionaires can raise any project-related issues on the platform.
- The issues raised in the GATI will be daily monitored by a team of officers in NHAI and will be constantly reviewed by the senior officers of NHAI and the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
10) National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP)
- NITI Aayog released its vision for the National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP)
- The platform aims to democratize access to publicly available government data.
- It will host the latest datasets from various government websites, present them coherently, and provide tools for analytics and visualization.
- NDAP will follow a user-centric approach and will enable data access in a simple and intuitive portal tailored to the needs of a variety of stakeholders.
11) Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar
Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar 2020 announced.
About the award:
- Awarded to recognize the excellent work done by individuals and institutions in India in the field of disaster management.
- Announced every year on 23rd January, the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- If the awardee is an institution, it shall receive a certificate and a cash prize of Rs. 51 lakhs. The Institution shall utilize this cash prize for Disaster Management related activities only.
- If the awardee is an individual, the winner shall receive a certificate and a cash prize of Rs. 5.00 lakhs.
- Only Indian nationals and Indian institutions can apply for the award.



Comments
Post a Comment