Current Affairs of Today Are
1) No extra charge on payments via RuPay, UPI
- Digital transactions made using RuPay credit cards or UPI QR codes will not attract additional charges for merchants or customers from the beginning of next year, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced
- All shops, business establishments and companies with an annual turnover of ₹50 crores or more have been mandated to offer these modes of payment to customers.
- The Department of Revenue will soon notify RuPay and UPI as the prescribed mode of payment for digital transactions without any Merchant Discount Rate (MDR)
What is the Merchant Discount Rate (MDR)?
The Merchant Discount Rate is the percentage of the digital transaction that a merchant pays to banks. This cost is often passed on to the customer.
Reason
- The decision to choose RuPay and UPI as the platforms which will not attract this levy may promote these homegrown digital payment pathways over those promoted by foreign companies, including VISA and MasterCard.
- In her budget speech in July, the Finance Minister had listed “BHIM UPI, UPIQR Code, Aadhaar Pay, certain Debit cards, NEFT, RTGS, etc.” as the lowcost digital modes of payment which could be offered without the imposition of MDR in order to promote a “less-cash” economy.
Effects on Bank without MDR
- RBI and banks will absorb these costs from the savings that will accrue to them on account of handling less cash as people move to these digital modes of payment.
- At that time, the Payments Council of India an industry lobby group had said an MDR waiver would hurt companies in the payments system.
- It argued that the cost should be borne by the government instead of banks, which would have no incentive to promote digital payments without MDR revenues.
2) Tests for an unmanned mission of ISRO
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) plans to fly the first unmanned test mission ahead of its ambitious crewed Gaganyaan mission by the end of 2020
- The unmanned flight will carry a humanoid
- Chandrayaan3 would be a copy of Chandrayaan2, except that it would not carry an orbiter. It would have a rover and a lander
- The Aeronautical Society of India (AeSI) to ISRO scientists to celebrate the 50th PSLV flight. The launch vehicle completed its 50th mission (PSLVc48) on December 11.
3) Mahagenco’s mining project
The Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC) an environmental panel of the Central government has
sent back the proposal to seek clearance to operate a coal mine in Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh, citing “hasty” submission of information that too “incomplete” and “incorrect”, during its meeting in early December, decided to “return the proposal in its present form” to the Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Limited (Mahagenco) to operate the Gare Palma Sector-II coal mine in the Tamnar block, with 22 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) open cast and 1.6 MTPA underground capacity.
Protest by Farmer
- Amid enduring protests by villagers against another coal mine project in their vicinity
- In September, during a public hearing for 2,245 project-affected families in 14 villages, residents highlighted the impact of the existing projects on groundwater and air quality, besides damage to fields due to spillage of fly ash, cracks in houses caused by blasting and fires in coal mines and stockpiles.
- Hundreds of them claimed that their consent was falsified and protested on the spot, resulting in the police booking 54 of them.
Reports on affecting areas
- Seeking clarifications and inputs on 20 points, the EAC has asked for compliance reports on the issues raised during the hearing with a “certain timeline and allocation” and a social impact assessment study for the proposed displacement of tribals and the Scheduled Castes.
- Furthermore, the company has to provide details relating to the impact on villages present in the core zone (not proposed to be displaced) of the mine, from where coal will be transported to three thermal power plants in Maharashtra to help “reduce the gap in demand and production of electricity” in the State.
- As for the impact on water, a “hydrological study and impact of mining activity on hydrology shall be submitted from the expert agency” and permission for the extraction of groundwater shall be obtained from the Central Ground Water Board.
- For using surface water from Kelo river for three initial years as proposed, the company will need to seek permission from the authority concerned
About Project
- The project, with an area of 2,583.48 hectares, will entail the diversion of 214.87 hectares of forest land.
- While 80% of the land (2077.69 hectares) is agricultural, settlements are spread across 90 hectares.
Environmental Issues
- Recently, a fivemember panel set up by the National Green Tribunal found the Tamnar-Gharghoda region, which has 13 coal mines and 12 power plants, close to exceeding its environmental carrying capacity
- The team also highlighted the negligence by the existing projects, with at least 27% of the fly ash from power plants being dumped in lowlying areas in a highly unscientific manner, destroying agricultural fields.
4) Child malnutrition: SSM- Population Health
Globally over 200 million children below five years of age are chronically malnourished causing persistent problems in middle and lowincome countries.
Though India’s National Family Health Surveys (NFHS) show that there has been a decline in child malnutrition numbers in the country, various studies show that the rate of decline is very slow, and India is still fighting a tough battle
Analysis of National Family Health Surveys (NFHS)
- A team from Harvard and Cambridge University has assessed districtlevel trends in the prevalence of malnutrition and how wealth disparity plays a role in five important malnutrition indicators such as stunting, underweight, wasting low birth weight, and anemia
- The researchers analyzed the NFHS4 data of 201516 and noted that among the four indicators, anemia was highly prevalent at 54.6%, across the poorest of the poor in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Telangana
- The team also placed each district under four categories disparity, pitfall, intensity or prosperity based on the overall burden and wealth disparity
- Wealth disparities in underweight children were seen across all districts with Gujarat, Jharkhand, and Bihar having the worst disparities and Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur having the least.
Underweight
- Underweight is highly correlated with child morbidity and is reflective of the current environmental and nutritional status of the child. Hence, underweight is arguably a more relevant and straightforward indicator to monitor for progress in child malnutrition
- The paper adds that for stunting and underweight, the north and central region of India which includes Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand were composed primarily of “pitfall” and “intensity” districts
National Nutrition Mission (NNM)
The team explains that though the Government of India’s new initiative National Nutrition Mission (NNM) has led to a progressive decline in child malnutrition, the decline has been slow and the improvements have not been equally distributed across the population.
Different strategies
Districts where the prevalence of malnutrition is uniformly high likely require a different intervention strategy compared with districts where prevalence is high but disproportionately shouldered amongst poorer households within the district. It is important to make sure progress on child nutrition is made both effectively and equitably
5) M.P. gets its first elephant colony
- Last November, elephants in herds, 38 of them, wandered into the forests of Bandhavgarh looking for food and water, like each year. A year on, they have stayed back in Madhya Pradesh for the first time
- over seasons and even bred two new calves, choosing not to return to the withering forests of north Chhattisgarh.
- The herd has found plenty of space, food, and water within the core area of the Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, and that’s why it may have stayed back
- The species is migratory, and often travels hundreds of miles to look for newer habitats with enough food and water
- The ‘Tiger State’ of Madhya Pradesh, which in the 2019 census recorded the most number of estimated tigers at 526, thus securing the title
- Ruling out the possibility of conflict between the herd and tigers both animals can coexist within the same territory. While one is a herbivore, the other is a carnivore, so there is no competition. The presence of elephants will not alter the movement of tigers in the area.
- Besides Bandhavgarh, two male elephants have strayed their way from Odisha into the forests of Narsingpur.
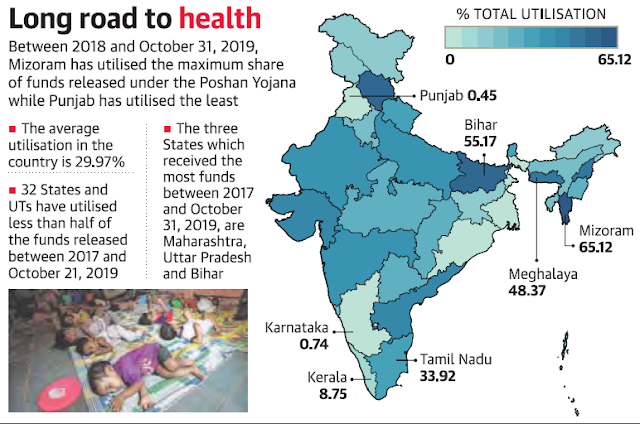
6) Poshan Abhiyaan
The State governments and the Union Territories utilized a mere 30% of the funds released under the Poshan Abhiyaan or the National Nutrition Mission since it was launched in 2017.
Barring Mizoram, Lakshadweep, Himachal Pradesh, and Bihar, none of the governments used even half of the sum granted in the past three years, according to an analysis of the data shared in Parliament.
About Poshan Abhiyaan
The Poshan Abhiyaan, the Centre’s flagship program, is aimed at improving nutritional outcomes among pregnant women, lactating mothers and children by reducing the level of stunting, underweight, anemia and low birth weight by 2022. It is meant to benefit more than 10 crore people
and was launched after a Cabinet decision on December 1, 2017, with a total budget of ₹9,046.17 crores for three years, 50% of which is through budgetary support, which is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the northeastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories without legislature. The remaining 50% is from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks. As a result, the Centre’s total share will be ₹2,849.54 crore
Distribution of Fund
- A total of ₹4,283 crores was disbursed by the Centre to different States and Union Territories.
- Of this, ₹1,283.89 crore, or only 29.97% of the funds granted, were utilized until October 31, 2019. Figures were not available for 2017 2018 as the scheme was launched at the fag end of the fiscal.
Performing States
The five best performers were Mizoram (65.12%), Lakshadweep (61.08%), Bihar (55.17%), Himachal Pradesh (53.29%) and Meghalaya (48.37%).
The worst five performers were Punjab (0.45%), Karnataka (0.74%), Kerala (8.75%), Jharkhand (13.94%) and Assam (23.01%)
7) Navy plans 24 submarines
- To strengthen its underwater fleet, the Navy plans to build 24 submarines, including six nuclear attack submarines, a parliamentary panel was told.
- The Navy also told the panel that Medium Refit Life Certification (MRLC) of submarine Sindhuraj was held up since the Russian side had not been able to submit bank guarantees and the integrity pact due to sanctions imposed by the U.S.
- The Navy said that there are presently 15 conventional submarines and two nuclear submarines in its fleet. The Navy has two nuclear submarines INS Arihant and INS Chakra, with the latter being leased from Russia.
- A majority of the conventional submarines are over 25 years old. Thirteen submarines age between 17 and 32 years
- The Indian Ocean Region, the area of operations of the Navy, has witnessed rising activities of the Chinese Navy. On its part, the Indian Navy has been revamping its infrastructure, including procuring new ships.
- Due to the delay in the submarine construction projects, including the Six Project 75 submarines at Mazagaon Docks, Mumbai, the Defence Ministry has approved Medium Refit cum Life Certification or MRLC of six older submarines, the report stated.
- With regards to the MRLC of the first submarine, work has already commenced in Russia on July 16 and is on schedule.
- The U.S. has imposed sanctions on Moscow citing several reasons ranging from the annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine to Russia with the recent one being the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act. The Russian side indicated L&T as their preferred partner for undertaking MRLC of the third Submarine Sindhuratna in India
8) Chief of the Defence Staff
- The government has issued a gazette modifying the Service Rules of the Army, Navy and Air Force to enable the appointment of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CDS) and fixing the upper age limit at 65
- The Centre amended the Army Rules 1954, Naval (Discipline and Miscellaneous Provisions) Regulations, 1965, Naval Ceremonial, Conditions of Service and Miscellaneous Regulations, 1963 and Air Force Regulations, 1964.
- However, the tenure of the CDS has not been fixed. The service chiefs have a tenure of three years or 62 years of age whichever is earlier and it remains unchanged.
- Last week, in anticipation of the announcement of the CDS, the Defence Ministry canceled the handing over ceremony of the Baton of the Chairman, Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC), to this week.
- The Union Cabinet had last week approved the creation of the post who will be a four-star General and will function as the Principal Military Adviser to the DefenceMinister and also as the Permanent Chairman of the COSC.

Comments
Post a Comment