Current Affairs of Today Are
1) Rajya Sabha Passes Citizenship Bill
- The Rajya Sabha passed the contentious Citizenship (Amendment) Bill (CAB), 2019, with 125 votes in favor and 99 against. The current strength of the Upper House is 240.
- The Bill amends the Citizenship Act, 1955, and for the first time, will grant citizenship based on religion to nonMuslim communities from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, who entered India on or before December 31, 2014. It was passed by the Lok Sabha on 9/12/19.
- The votes of the AIADMK, the Janata Dal (United) and the Biju Janata Dal were key in helping the BJP-led government push the Bill through in the Upper House. Members of former BJP ally
- Shiv Sena participated in the debate but did not vote.
- Two MPs of the Nationalist Congress Party and the Bahujan Samaj Party were absent
Negative Side of The Bill
- The government of violating the provisions of the Constitution.
- The legislation could be challenged on legal grounds.
- Government Said “lakhs and crores” of people would benefit from the Bill.
- The Director of the Intelligence Bureau had said in a report that around 31,000 people would be the immediate beneficiaries.
- So far only 4,400 people have cited religious persecution as grounds to get citizenship
Major Challenges
- How the government would differentiate between illegal migrants and those persecuted on religious grounds?
- The government was forcing people to lie that they had come from Bangladesh as they always claimed they are Indians.
Citizenship For Muslim
Any Muslim could apply for citizenship through the usual channels and in the past five years, 566 persons from Pakistan were granted citizenship.
2) 50th PSLV launch
India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) marked its ‘Golden Jubilee’ launch on Wednesday by injecting India’s advanced radar imaging satellite RISAT-2BR1 and nine other customer satellites from Japan, Italy, Israel, and the U.S. into their intended orbits.
PSLV transformation in 26 years
- The PSLV, which has a history of successful launches of payloads that include Chandrayaan-1, Mars Orbiter Mission and the space recovery mission from the refurbished first launchpad, marking the 50th launch for the vehicle.
- ISRO also achieved a major milestone of 75 launches from there spaceport
- Initially, the PSLV had a carrying capacity of 850 kg, and over the years it has been enhanced to 1.9 tonnes. The PSLV is very versatile, having various mission options
- The PSLV had helped take payloads into almost all the orbits in space, including the GeoStationary Transfer Orbit (GTO), the moon and Mars, and would soon be launching a mission to the Sun
- In the last 26 years, the PSLV had lifted more than 52 tonnes into space, of which about 17% were for commercial customers.
- ISRO Chairman K. Sivan also released a book commemorating the 50 launches and the scientists involved in them
- The PSLV has failed only twice the maiden flight of the PSLV D1 in September 1993 and the PSLV C-39 in August 2017.
About RISAT-2BR1
- RISAT-2BR1 will be used for agriculture, forestry, disaster management support and national security.
- ISRO will launch the next version of RISAT within the next two months
3) Andhra Pradesh Cabinet clears Disha Bill
- The Andhra Pradesh Cabinet cleared the A.P. Disha Bill, 2019 (A.P. Criminal Law (Amendment) Bill, 2019) paving the way for awarding the death penalty for the offenses of rape and gangrape and expediting the verdict in trials of such cases to 21 days. The legislation is to be tabled in the ongoing session of the Assembly
- The Cabinet also gave its nod for introduction of the A.P. Special Court for Specified Offenses against Women and Children Bill, 2019, for dealing with offenses against women and children, including rape and gangrape, acid attacks, stalking, voyeurism, sexual harassment, and cases under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act.
- The A.P. Criminal Law (Amendment) Bill, 2019, envisages the completion of investigation and trial in seven and 14 working days respectively, where there is adequate conclusive evidence, and reducing the total judgment time to 21 days from the existing four months
- The proposed laws seek to amend relevant provisions in the Indian Penal Code, 1860, and the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, and to introduce Sections 354E and 354F in the IPC for dealing with harassment of women through social media and sexual assault of children respectively.
- Under Section 354-E (harassment of women through social media, digital mode or any other form), it has been proposed to sentence the guilty to imprisonment for up to two years on first conviction and four years on subsequent convictions.
- Under Section 354-F (molestation / sexual assault), imprisonment is sought to be increased to a minimum of five years and a maximum of seven years.

4) Survey of butterfly species in the Papikonda National Park (PNP)
- The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department and experts from Kerala and northeastern States will begin the first survey of butterfly species in the Papikonda National Park (PNP).
- The PNP spreads over 1012.86 sq.km. in East and West Godavari districts
- The experts, led by Keralabased environmental forum Warblers and Waders, will carry out the survey to record all butterfly species, and also conduct a study on migratory species in the national park in the Papikonda hill range in the Eastern Ghats.
- The fourday survey, from December 12 to 15, is the maiden survey during which the entire national park will be explored, documenting the butterfly species
- The exercise will offer a picture of the existing biodiversity of the park. The diversity of butterfly species would be considered as a health indicator of the park. Declared as a national park in 2018, preliminary studies have recorded over 80 species of butterflies.
- The park is home to 121 butterfly species as per their internal studies.
5) Heavy metals contaminating India’s rivers
- Samples taken from two-thirds of the water quality stations spanning India’s major rivers showed contamination by one or more heavy metals, exceeding safe limits set by the Bureau of Indian Standards.
- The findings are part of a report, which is the third edition of an exercise conducted by the Central Water Commission (CWC) from May 2014 to April 2018.
- Samples from only one-third of water quality stations were safe. The rest, or 287 (65%) of the 442 sampled, were polluted by heavy metals. Samples from 101 stations had contamination by two metals, six stations saw contamination by three metals.
- Iron emerged as the most common contaminant with 156 of the sampled sites registering levels of the metal above safe limits. None of the sites registered arsenic levels above the safe limit.

Metal in water good or bad?
- The presence of metals in drinking water is to some extent unavoidable and certain metals, in trace amounts, required for good health. However, when present above safe limits, they are associated with a range of disorders.
- Longterm exposure to the abovementioned heavy metals may result in slowly progressing physical, muscular, and neurological degenerative processes that mimic Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, muscular dystrophy, and multiple sclerosis.
Survey on River
- The other major contaminants found in the samples were lead, nickel, chromium, cadmium and copper.
- The study spanned 67 rivers in 20 river basins. Lead, cadmium, nickel, chromium, and copper contamination were more common in non-monsoon periods while iron, lead, chromium and copper exceeded ‘tolerance limits’ in monsoon periods most of the time. “Arsenic and zinc are the two toxic metals whose concentration was always obtained within the limits throughout the study period.
- Not all rivers are equally sampled. Several rivers have only been sampled at a single site whereas others such as the Ganga, the Yamuna, and the Godavari are sampled at multiple sites. Marked variation was found in contamination levels depending on the season.
- Samples were collected in three different seasons: pre-monsoon, monsoon, and post-monsoon.
Sources
The main sources of heavy metal pollution are mining, milling, plating and surface finishing industries that discharge a variety of toxic metals into the environment
6) International Financial Services Centres (IFSC) Authority Bill, 2019
- The Lok Sabha passed the International Financial Services Centres (IFSC) Authority Bill, 2019 which provides for the establishment of an authority to develop and regulate the financial services market.
- The unified authority would act as a single-window of regulation. She added that all the laws of the land, including the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, would apply and would be audited by the CVC and the CAG.
- The International Financial Services Centres Authority Bill, 2019, was introduced in the Lok Sabha after withdrawal from the Rajya Sabha. Currently, the banking, capital markets and insurance sectors in IFSC are regulated by multiple regulators. The Bill seeks to amend 14 Acts, including the SEBI Act, the IRDA Act, and the PFRDA Act.
7) Code on Social Security Bill, 2019
- Labour Minister Santosh Gangwar introduced the Code on Social Security, 2019, in the Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to amend and consolidate laws relating to the social security of employees, subsuming eight Central laws.
- The eight Central Labour Acts, namely Employees' Compensation Act, 1923; Employees State Insurance Act, 1948, Employees Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952; Maternity Benefit Act, 1961; Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972; Cine Workers Welfare Fund Act, 1981; Building and Other Construction Workers Cess Act, 1996 and Unorganised Workers Social Security Act, 2008, are to be subsumed under the new law
- The new code will give the option for the reduction of Provident Fund contribution by employees in some sectors from 12% to 10%. The reduction will not apply to employers and has been done solely to increase the take-home pay of employees.
- The Bill also proposes to set up a social security fund using the funds available under corporate social responsibility, to provide welfare benefits such as pensions and death and disability benefits. The Bill also has a clause to make fixed-term contract workers eligible for gratuity on a prorata basis.
8) Bougainville- the world’s newest country
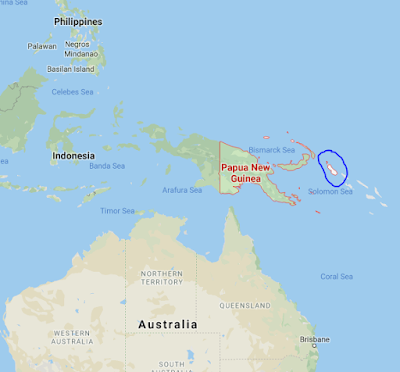 |
| Blue Colour highlighted Island is Bougainville |
- Voters backing Bougainville’s independence from Papua New Guinea have won a landslide referendum victory, according to results a major step toward the troubled isles becoming the world’s newest nation
- Chairman of the Bougainville Referendum Commission Bertie Ahern declared that 1,76,928 people around 98% of voters had backed independence with just 3,043 supporting the option of remaining part of Papua New Guinea with more autonomy.
- The historic vote caps a decadeslong peace process and a long recovery from a brutal civil war between Bougainville rebels, Papua New Guinea security forces and foreign mercenaries that ended in 1998 and left up to 20,000 people dead 10% of the population.
9) Myanmar genocide allegations
Myanmar’s former prodemocracy icon Aung San Suu Kyi denied that her country’s armed forces committed genocide against the Rohingya minority, telling the U.N.’s top court that the exodus of hundreds of thousands of Muslims was the unfortunate result of a battle with insurgents.
Which Country brought legal action against Myanmar?
The Gambia, which brought the legal action against Myanmar on behalf of the 57 country Organization of Islamic Cooperation allegations that the army had killed civilians, raped women and torched houses in 2017 in what Myanmar’s accusers describe as a deliberate campaign of ethnic
cleansing and genocide that saw more than 700,00 Rohingya flee to neighboring Bangladesh.
10) International Seminar on Climate Smart Farming Systems
- The three days ‘International Seminar on Climate Smart Farming Systems’ for BIMSTEC countries organized by the Department of Agricultural Research & Education, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmer’s Welfare and Indian Council of Agricultural Research began today in New Delhi. Participants from all the Seven BIMSTEC Countries viz. Bhutan, Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and BIMSTEC Secretariat are attending the Seminar.
- The seminar is being organized as a Government of India initiative as announced earlier by the Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi at the 4th BIMSTEC Summit at Kathmandu on 30-31st August 2019. The objective of this International Seminar is to have experience sharing to enable improvement of tropical smallholder farming systems for greater productivity and resilience to climate change through ecological approaches. Some of the success stories shall be shared as case studies for the benefit of the BIMSTEC countries. The Seminar would have invited lectures and sharing of experiences, visits to state-of-art facilities and field visits to have first-hand experiences.
About BIMSTEC
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional organization comprising of seven member states in South Asia and Southeast Asia lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of Bay of Bengal constituting a contiguous regional unity. This sub-regional organization came into being on June 6, 1997, through the Bangkok Declaration

Comments
Post a Comment