Current Affairs of Today are
1) Tap water quality released by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)

- Delhi's s tap water is the most unsafe among 21 State capitals.
- The national capital is at the very bottom of the list, in a ranking based on tap water quality released by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
- It is among 13 cities where all tested samples failed to meet the BIS norms for piped drinking water, including Kolkata, Chennai, Bengaluru, Jaipur, and Lucknow
- Mumbai is the only city where all samples of tap water met all the tested parameters under the Indian Standard 10500:2012 (specification for drinking water).
 Jal Jeevan Mission
Jal Jeevan Mission
The Government aims to provide safe piped water to all households by 2024, with promising to spend over ₹3.5 lakh crore on the scheme.
Result of Study
The studies showed that even in urban areas, which are connected to the piped water network, there is no guarantee that the water is safe for consumption
About BIS Standards Tap water quality
The BIS standard involves 48 different parameters. Samples are being tested under 28 parameters so far, leaving out parameters related to radioactive substances and free residual chlorine.
Samples are undergoing physical and organoleptic tests (which identify the odor, turbidity and pH levels), as well as chemical tests and virological, bacteriological and biological tests (which identify harmful organisms and disease carriers).
2) 6th Joint Monitoring Mission ( JMM 2019)
- The sixth Joint Monitoring Mission ( JMM 2019) of the Union government and the World Health Organization on the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) has lauded Kerala for being right on track to achieve TB elimination by 2025.
- The State will now have to focus better on strengthening its diagnostic services and the training component so that every case in the community is picked up. Hence, more molecular diagnostic services (CBNAAT /Genexpert machines) are needed
- The JMM team felt that the State has allowed its Intermediate Reference Laboratory (IRL) in the capital (where advanced tests are done) to languish and that very little has been done to improve the technical capacity or human resource.
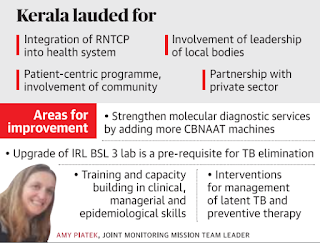
About Joint Monitoring Mission ( JMM 2019)
The sixth JMM, comprising 24 members, is visiting Kerala as part of the midyear assessment of India’s National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination, 2017-25
3) The Wastelands Atlas
- The Wastelands Atlas, prepared in collaboration with the National Remote Sensing Centre and released recently by the Land Resources Department uses satellite data to measure the extent of 23 different types of wastelands and tracks the impact of reclamation efforts.
- India’s conversion of more
- than 14,000 square km of ‘wasteland’ mostly dense scrub, glacial areas, sands or marshland — into productive use between 2008-09 and 2015-16, and the government’s target to restore 26 million hectares of wasteland and degraded land by 2030 risks affecting the livelihoods of pastoralists, fishermen and nomadic farmers who are often dependent on these traditional “commons” land.
- The country saw a net conversion of 8,404 sq. km. Over half that land lies in Rajasthan, where a net change of 4,803 sq. km was seen, with large areas of scrub and sands brought under the plough and converted to cultivated cropland. The State also has extensive solar parks set up in its wastelands, thus converting them to industrial use in the production of renewable energy. Uttar Pradesh and Bihar also saw high levels of net conversion.
Why it is needed?
The government has been encouraging wasteland conversion, pointing out that while India has 18% of the world’s population, it only has 2.4% of the land area. To ensure food security, there is an urgent need to improve the productivity of existing cultivated lands and to bring additional land under plough. The wastelands which are unutilized and have the potential to produce food grain and provide vegetation cover may significantly contribute to this endeavor
The negative side of wasteland conversion
- However, such conversions could impact livelihoods. Pastoral communities depend on common grazing land, gatherers and nomadic farmers depend on scrub forest and open scrubland for shifting cultivation, while fishermen can make a living off waterlogged and marshy areas. These areas protect unique biodiversity resources, which could be destroyed when development occurs.
- Chennai had paid a heavy price for converting wastelands such as the Pallikaranai marsh or the Ennore creek backwaters, into industrial, builtup areas. The flooding in recent seasons happened because marshland was treated as waste rather than a valuable buffer. The backwaters protect inland water resources from encroaching salinity and seawater inundation, as well as storing water for dry seasons.
- The backwaters protect inland water resources from encroaching salinity and seawater inundation, as well as storing water for dry seasons
Where did Idea Wasteland come from?
It was the East India company that first categorized these areas as a wasteland, as they produce no tangible revenue
4) Gotabaya wins in the presidential poll of Sri Lanka
Gotabaya Rajapaksa, an Opposition candidate in Sri Lanka’s presidential election, emerged as a winner, securing 52.25 %.
Mr. Rajapaksa beat the government’s candidate Sajith Premadasa who got nearly 42% of the vote share. Mr. Rajapaksa will be sworn in as Sri Lanka’s seventh executive president on Monday in the historic city of Anuradhapura, his Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna (SLPP or People’s Party)
5) 6th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)
Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh held a bilateral meeting with US Secretary of Defence Dr. Mark T Esper on the sidelines of ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) in Bangkok
Shri Rajnath Singh added that there is growing convergence between India and the US in the Indo-Pacific region and India’s vision for Indo-Pacific is for a free & open, peaceful, prosperous and inclusive region supported by a rules-based order and respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity. Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is central to India’s vision of Indo-Pacific. Both countries are working together in the area of Maritime security including elements such as joint exercises, Humanitarian Assistance, and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations and Maritime Domain Awareness.
6) Home Minister launches winter-grade diesel suitable for extreme winters of up to -30 degree Celcius for Ladakh Region
 Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah presided over a function to launch a special winter-grade diesel, developed by Indian Oil Corporation (Indian Oil), for the high-altitude regions of Ladakh
Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah presided over a function to launch a special winter-grade diesel, developed by Indian Oil Corporation (Indian Oil), for the high-altitude regions of Ladakh Need for it
Motorists in high-altitude sectors like Ladakh, Kargil, Kaza, and Keylong face the problem of freezing of diesel in their vehicles when winter temperatures drop to as low as -30o Celsius. Indian Oil has come up with an innovative solution to this problem by introducing a special winter-grade diesel with a low pour-point of -33o Celsius, which does not lose its fluidity function even in extreme winter conditions.
What is Winter-Grade Diesel?
- Winter diesel fuel (also known as winter diesel, alpine diesel, or winterized diesel (AE)) refers to diesel fuel enhanced to prevent it from gelling in cold weather conditions. In general, it is achieved by treatment with additives that change the low-temperature characteristics of the fuel.
- Diesel fuel is prone to waxing or gelling in cold weather; both are terms for the solidification of diesel oil into a partially crystalline state. Below the Cloud Point, the fuel begins to develop solid wax particles giving it a cloudy appearance. The presence of solidified waxes thickens the oil and clogs fuel filters and injectors in engines. The crystals build up in the fuel line (especially in fuel filters) until the engine is starved of fuel, causing it to stop running.
- The Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP) is based on a standardized test that indicates the rate at which diesel fuel will flow through a standardized filtration device in a specified length of time when cooled under certain conditions. Similarly, the "Low-Temperature Flow Test" (ASTM D4539) indicates the winter performance of diesel with improver additives. Note that both the CFPP and LTFT temperature is some degrees above the Pour Point temperature at which diesel fuel loses its fluid character and that pumps would stop operating.



Comments
Post a Comment